Conditional inactivation of presenilin 1 prevents amyloid accumulation and temporarily rescues contextual and spatial working memory impairments in amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice
- PMID: 16033885
- PMCID: PMC6725351
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1247-05.2005
Conditional inactivation of presenilin 1 prevents amyloid accumulation and temporarily rescues contextual and spatial working memory impairments in amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice
Abstract
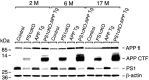
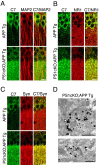
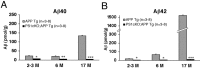
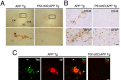
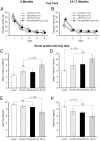
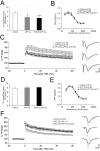
Accumulation of beta-amyloid (Abeta) peptides in the cerebral cortex is considered a key event in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Presenilin 1 (PS1) plays an essential role in the gamma-secretase cleavage of the amyloid precursor protein (APP) and the generation of Abeta peptides. Reduction of Abeta generation via the inhibition of gamma-secretase activity, therefore, has been proposed as a therapeutic approach for AD. In this study, we examined whether genetic inactivation of PS1 in postnatal forebrain-restricted conditional knock-out (PS1 cKO) mice can prevent the accumulation of Abeta peptides and ameliorate cognitive deficits exhibited by an amyloid mouse model that overexpresses human mutant APP. We found that conditional inactivation of PS1 in APP transgenic mice (PS1 cKO;APP Tg) effectively prevented the accumulation of Abeta peptides and formation of amyloid plaques and inflammatory responses, although it also caused an age-related accumulation of C-terminal fragments of APP. Short-term PS1 inactivation in young PS1 cKO;APP Tg mice rescued deficits in contextual fear conditioning and serial spatial reversal learning in a water maze, which were associated with APP Tg mice. Longer-term PS1 inactivation in older PS1 cKO;APP Tg mice, however, failed to rescue the contextual memory and hippocampal synaptic deficits and had a decreasing ameliorative effect on the spatial memory impairment. These results reveal that in vivo reduction of Abeta via the inactivation of PS1 effectively prevents amyloid-associated neuropathological changes and can, but only temporarily, improve cognitive impairments in APP transgenic mice.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neuronal deficiency of presenilin 1 inhibits amyloid plaque formation and corrects hippocampal long-term potentiation but not a cognitive defect of amyloid precursor protein [V717I] transgenic mice.J Neurosci. 2002 May 1;22(9):3445-53. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-09-03445.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 11978821 Free PMC article.
-
APP processing and synaptic plasticity in presenilin-1 conditional knockout mice.Neuron. 2001 Sep 13;31(5):713-26. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(01)00417-2. Neuron. 2001. PMID: 11567612
-
Amyloid-beta deposition is associated with decreased hippocampal glucose metabolism and spatial memory impairment in APP/PS1 mice.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2004 May;63(5):418-28. doi: 10.1093/jnen/63.5.418. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2004. PMID: 15198121
-
Genes and mechanisms involved in beta-amyloid generation and Alzheimer's disease.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1999;249(6):266-70. doi: 10.1007/s004060050098. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10653281 Review.
-
Role of presenilin in gamma-secretase cleavage of amyloid precursor protein.Exp Gerontol. 2000 Jul;35(4):453-60. doi: 10.1016/s0531-5565(00)00111-x. Exp Gerontol. 2000. PMID: 10959033 Review.
Cited by
-
Minocycline reduces neuroinflammation but does not ameliorate neuron loss in a mouse model of neurodegeneration.Sci Rep. 2015 May 22;5:10535. doi: 10.1038/srep10535. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26000566 Free PMC article.
-
Inactivation of Presenilin in inhibitory neurons results in decreased GABAergic responses and enhanced synaptic plasticity.Mol Brain. 2021 May 25;14(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s13041-021-00796-5. Mol Brain. 2021. PMID: 34034776 Free PMC article.
-
Transnasal delivery of human A-beta peptides elicits impaired learning and memory performance in wild type mice.BMC Neurosci. 2016 Jul 4;17(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s12868-016-0280-9. BMC Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27377996 Free PMC article.
-
β-Arrestins as potential therapeutic targets for Alzheimer's disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2013 Dec;48(3):812-8. doi: 10.1007/s12035-013-8469-8. Epub 2013 May 16. Mol Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23677646 Review.
-
APP dyshomeostasis in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease: implications for current drug targets.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024 Jun 29;16(1):144. doi: 10.1186/s13195-024-01504-w. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38951839 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amtul Z, Lewis PA, Piper S, Crook R, Baker M, Findlay K, Singleton A, Hogg M, Younkin L, Younkin SG, Hardy J, Hutton M, Boeve BF, Tang-Wai D, Golde TE (2002) A presenilin 1 mutation associated with familial frontotemporal dementia inhibits γ-secretase cleavage of APP and Notch. Neurobiol Dis 9: 269-273. - PubMed
-
- Borchelt DR, Thinakaran G, Eckman CB, Lee MK, Davenport F, Ratovitsky T, Prada C-M, Kim G, Seekins S, Yager D, Slunt HH, Wang R, Seeger M, Levey AI, Gandy SE, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Price DL, Younkin SG, Sisodia SS (1996) Familial Alzheimer's disease-linked presenilin 1 variants elevate Aβ1-42/1-40 ratio in vitro and in vivo Neuron 17: 1005-1013. - PubMed
-
- Cai D, Leem JY, Greenfield JP, Wang P, Kim BS, Wang R, Lopes KO, Kim SH, Zheng H, Greengard P, Sisodia SS, Thinakaran G, Xu H (2003) Presenilin-1 regulates intracellular trafficking and cell surface delivery of β-amyloid precursor protein. J Biol Chem 278: 3446-3454. - PubMed
-
- Chapman P, White G, Jones M, Cooper-Blacketer D, Marshall V, Irizarry M, Younkin L, Good M, Bliss T, Hyman B, Younkin S, Hsiao K (1999) Impaired synaptic plasticity and learning in aged amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice. Nat Neurosci 2: 271-276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
