Vitamin A for non-measles pneumonia in children
- PMID: 16034908
- PMCID: PMC6991929
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003700.pub2
Vitamin A for non-measles pneumonia in children
Abstract
Background: Acute respiratory infections, mostly in the form of pneumonia, are the leading causes of death in children under five years of age in developing countries. Some clinical trials have demonstrated that vitamin A supplementation reduces the severity of respiratory infection and mortality in children with measles.
Objectives: To determine whether adjunctive vitamin A is effective in infants and children diagnosed with non-measles pneumonia.
Search strategy: We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (The Cochrane Library Issue 4, 2004); MEDLINE (1996 to November Week 3, 2004); EMBASE (1990 to September 2004); LILACS (9 January 2004); CINAHL (1990 to November 2004); Biological Abstracts (1990 to November 2004) and Current Contents (1990 to September 2004); and the Chinese Biomedicine Database (CBM) (1994 to November 2004).
Selection criteria: Only parallel-arm, randomised and quasi-randomised controlled trials in which children (younger than 15 years old) with non-measles pneumonia were treated with adjunctive vitamin A were included.
Data collection and analysis: Two authors independently extracted data and assessed trial quality. Study authors were contacted for additional information.
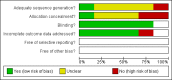
Main results: Five trials involving 1453 infants and children were included. There was no significant reduction in the mortality associated with pneumonia in children treated with vitamin A compared to those who were not (pooled odds ratio (OR) 1.49; 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.66 to 3.35). In addition, there was a lack of a statistically significant effect on duration of stay in hospital (weighted mean difference (WMD) 0.08; 95% CI -0.43 to 0.59). Vitamin A was associated with a 39% reduction in antibiotic firstline failure (OR 0.65; 95% CI 0.42 to 1.01). Children receiving vitamin A were no more likely to experience vomiting (OR 0.77; 95% CI 0.45 to 1.33), diarrhoea (OR 0.57; 95% CI 0.31 to 1.05), bulging of the fontanelles (OR 8.25; 95% CI 0.44 to 155.37) or irritability (OR 0.93, 95% CI 0.56 to 1.57) than those not receiving vitamin A. There was no statistical significance between vitamin A and placebo groups (OR 0.90; 95% CI -1.10 to 2.90) in chest x-ray results. Disease severity after supplementary high-dose vitamin A was significantly worse in children who received vitamin A compared with placebo. Low-dose vitamin A was associated with a significant reduction in the recurrent rate of bronchopneumonia (OR 0.12; 95% CI 0.03 to 0.46).
Authors' conclusions: The evidence did not suggest a significant reduction with vitamin A adjunctive treatment in mortality, measures of morbidity, nor an effect on the clinical course of pneumonia in children with non-measles pneumonia. However, not all studies measured all outcomes, limiting the number of studies that could be incorporated into the meta-analyses, so that there may have been a lack of statistical power to detect statistically significant differences.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures
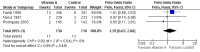
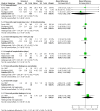

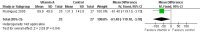




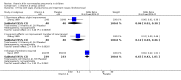
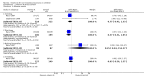

Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
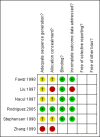
Fawzi 1998 {published data only}
-
- Fawzi W, Chalmers T, Herrera M, Mosteller F. Vitamin A supplementation and severity of pneumonia in children admitted to the hospital in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1998;68:187‐92. - PubMed
Liu 1997 {published data only}
-
- Liu XH, Yin SA, Li G, Gao HY, Xu QM. A clinical observation on supplementing selenium and vitamin A for mycoplasma pneumonia in children. Journal of Chinese Children Health Care 1997;5(4):239‐40.
Nacul 1997 {published data only}
Rodriguez 2005 {published data only}
-
- Rodriguez A, Hamer DH, Rivera J, Acosta M, Salgado G, Gordillo M. Effects of moderate doses of vitamin A as an adjunct to the treatment of pneumonia in underweight and normal‐weight children: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2005;82(5):1090‐6. - PubMed
Stephensen 1998 {published data only}
-
- Stevensen C, Franchi L, Hernandez H, Campos M, Gilman R, Alvarez J. Adverse effects of high‐dose vitamin A supplements in children hospitalized with pneumonia. Pediatrics 1998;101:1‐8. - PubMed
Zhang 1999 {published data only}
-
- Zhang J. Observation for vitamin A as a complementary agent in the treatment of bronchopneumonia. Journal of Jining Medical College 1999;22(2):55.
References to studies excluded from this review
Anonymous 1991 {published data only}
-
- Anonymous. Vitamin A administration reduces mortality and morbidity from severe measles in populations nonendemic for hypovitaminosis. Nutrition Reviews 1991;49:89‐91. - PubMed
Barreto 1994 {published data only}
-
- Barreto ML, Santos LM, Assis AM, Araujo MP, Farenzena GG, Santos PA, et al. Effect of vitamin A supplementation on diarrhoea and acute lower‐respiratory‐tract infections in young children in Brazil. Lancet 1994;344:228‐31. - PubMed
Basu 2003 {published data only}
Bhandari 1997 {published data only}
Biesalski 2001 {published data only}
-
- Biesalski HK. Importance of vitamin a for lung development. Monatsschrift fur Kinderheilkunde 2001;149(Suppl):25‐32.
Biswas 1994 {published data only}
-
- Biswas R, Biswas AB, Manna B, Bhattacharya SK, Dey R, Sarkar S. Effect of vitamin A supplementation on diarrhoea and acute respiratory tract infection in children. A double blind placebo controlled trial in a Calcutta slum community. European Journal of Epidemiology 1994;10:57‐61. - PubMed
Bresee 1996 {published data only}
-
- Bresee J, Fischer M, Dowell S, Johnston B, Biggs V, Levine, R, et al. Vitamin A therapy for children with respiratory syncytial virus infection: a multicenter trial in the United States. Pediatric Infectious Diseases Journal 1996;15:777‐82. - PubMed
Buyukgebiz 1990 {published data only}
-
- Buyukgebiz B, Ozalp I, Oran O. Investigation of serum vitamin A levels of children who had a history of recurrent diarrhoea and acute respiratory infections in Ankara. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics 1990;36:251‐5. - PubMed
Chen 2005 {published data only}
-
- Chen Y, Hua Z, Di P, Xu T. Effect of intravenously administered liposomal vitamin A in neonatal pneumonia. Journal of Pediatric Phamacy 2005;11(6):11‐3.
Coles 2001 {published data only}
-
- Coles CL, Rahmathullah L, Kanungo R, Thulasiraj RD, Katz J, Santhosham M, et al. Vitamin A supplementation at birth delays pneumococcal colonization in South Indian infants. Journal of Nutrition 2001;131:255‐61. - PubMed
Coutsoudis 2000 {published data only}
-
- Coutsoudis A, Adhikari M, Pillay K, Kuhn L, Coovadia HM. Effect of vitamin A supplementation on morbidity of low‐birth‐weight neonates. South African Medical Journal 2000;90:730‐6. - PubMed
Daulaire 1992 {published data only}
Dibley 1996 {published data only}
-
- Dibley MJ, Sadjimin T, Kjolhede CL, Moulton LH. Vitamin A supplementation fails to reduce incidence of acute respiratory illness and diarrhea in preschool‐age Indonesian children. Journal of Nutrition 1996;126:434‐42. - PubMed
Donnen 1998 {published data only}
-
- Donnen P, Dramaix M, Brasseur D, Bitwe R, Vertongen F, Hennart P. Randomized placebo‐controlled clinical trial of the effect of a single high dose or daily low doses of vitamin A on the morbidity of hospitalized, malnourished children. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1998;68:1254‐60. - PubMed
Dowell 1996 {published data only}
-
- Dowell S. Treatment of respiratory syncytial virus infection with vitamin A: a randomized, placebo‐controlled trail in Santiago, Chile. Pediatrics Infectious Diseases 1996;15:782‐6. - PubMed
Dudley 1997 {published data only}
-
- Dudley L, Hussey G, Huskissen J, Kessow G. Vitamin A status, other risk factors and acute respiratory infection morbidity in children. South African Medical Journal 1997;87:65‐70. - PubMed
Fauveau 1992 {published data only}
Fawzi 1995 {published data only}
-
- Fawzi WW, Herrera MG, Willett WC, Nestel P, Amin A, Mohamed KA. Dietary vitamin A intake and the incidence of diarrhea and respiratory infection among Sudanese children. Journal of Nutrition 1995;125:1211‐21. - PubMed
Fawzi 1999 {published data only}
-
- Fawzi WW, Mbise RL, Hertzmark E, Fataki MR, Herrera MG, Ndossi G, et al. A randomized trial of vitamin A supplements in relation to mortality among human immunodeficiency virus‐infected and uninfected children in Tanzania. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 1999;18:127‐33. - PubMed
Fawzi 2000 {published data only}
-
- Fawzi WW, Mbise R, Spiegelman D, Fataki M, Hertzmark E, Ndossi G. Vitamin A supplements and diarrheal and respiratory tract infections among children in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. Journal of Pediatrics 2000;137:660‐7. - PubMed
Fu 2005 {published data only}
-
- Fu Y. The usage of Vitamin A for respiratory tract infection in children. Central Plains Medical Journal 2005;32(10):25‐6.
Ghana VAST team 1993 {published data only}
-
- Ghana VAST Study Team. Vitamin A supplementation in northern Ghana: effects on clinic attendances, hospital admissions, and child mortality. Lancet 1993;342:7‐12. - PubMed
Hadi 1999 {published data only}
-
- Hadi H, Stoltzfus RJ, Moulton LH, Dibley MJ, West KP Jr. Respiratory infections reduce the growth response to vitamin A supplementation in a randomized controlled trial. International Journal of Epidemiology 1999;28:874‐81. - PubMed
Humphrey 1996 {published data only}
-
- Humphrey JH, Agoestina T, Wu L, Usman A, Nurachim M, Subardja D, et al. Impact of neonatal vitamin A supplementation on infant morbidity and mortality. Journal of Pediatrics 1996;128:489‐96. - PubMed
Julien 1999 {published data only}
-
- Julien M, Gomes A, Varandas L, Lerberghe W, Rodrigues P, Malveiro F. A randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled clinical trial of vitamin A in Mozambican children hospitalized with non‐measles acute lower respiratory tract infections. Tropical Medicine and International Health 1999;4:794‐800. - PubMed
Junhong 1997 {published data only}
-
- Junhong Z, Youqing Q, Deyuan Z. The study of the effect of massive dose vitamin A intervention to recurrent respiratory infection. Acta Nutrimenta Sinica 1997;19:291‐3.
Kao 1996 {published data only}
-
- Kao Y, Yu X, Li Z. Vitamin A as a complementary agent in the treatment of pneumonia in children. Journal of Zhejiang Prevention Medicine 1996;8(6):39‐40.
Kartasasmita 1995 {published data only}
-
- Kartasasmita CB, Rosmayudi O, Deville W, Demedts M. Plasma retinol level, vitamin A supplementation and acute respiratory infections in children of 1‐5 years old in a developing country. Respiratory Diseases Working Group. Tubercle and Lung Disease 1995;76:563‐9. - PubMed
Khandait 2000 {published data only}
-
- Khandait DW, Vasudeo ND, Zodpey SP, Kumbhalkar DT. Risk factors for subclinical vitamin A deficiency in children under the age of 6 years. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics 2000;46:239‐41. - PubMed
Kjolhede 1995 {published data only}
-
- Kjolhede C, Chew F, Gadomski A, Marroquin D. Clinical trial of vitamin A as adjuvant treatment for lower respiratory tract infections. Journal of Pediatrics 1995;126:807‐12. - PubMed
Li 2004 {published data only}
-
- Li Y. Observation for vitamin A as a complementary agent in the treatment of new born baby with pneumonia. Central Plains Medical Jounal 2004;31(9):40‐1.
Lie 1993 {published data only}
-
- Lie C, Ying C, Wang EL, Brun T, Geissler C. Impact of large‐dose vitamin A supplementation on childhood diarrhoea, respiratory disease and growth. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1993;47:88‐96. - PubMed
Lin 1999 {published data only}
-
- Lin L, Lu X. Observation on curative of vitamin AD as an adjuvant for premature delivered infant infectious pneumonia. Journal of Huangshi Polytechnic College 1999;15(2):36‐7.
Liu 2002 {published data only}
-
- Liu JM, Gu XY. Effect of vitamin A as an adjuvant drug in the treatment of bronchopneumonia. Modern Practice Medicine 2002;14(6):302.
Lloyd 1991 {published data only}
-
- Lloyd‐Puryear MA, Mahoney J, Humphrey JH, Mahoney F, Siren N, Moorman C, et al. Vitamin A deficiency in Micronesia: A statewide survey in Chuuk. Nutrition Research 1991;11:1101‐10.
Long 2006 {published data only}
-
- Long KZ, Montroya Y, Hertzmark E, Santos JI, Rosado JL. A double‐blind, randomized, clinical trial of the effect of vitamin A and zinc supplementation on diarrheal disease and respiratory tract infections in children in Mexico City, Mexico. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2006;83(3):693‐700. [MEDLINE: ; ISSN:0002‐9165] - PubMed
Long 2007 {published data only}
-
- Long KZ, Rosado JL, DuPont HL, Hertzmark E, Santos JI. Supplementation with vitamin A reduces watery diarrhoea and respiratory infections in Mexican children. British Journal of Nutrition 2007;97(2):337‐43. - PubMed
Ma 2000 {published data only}
-
- Ma C. Effects observation of vitamin A in the complementary treatment of respiratory syncytial virus pneumonia. Clinical Medicine 2000;20(3):45‐6.
Mahalanabis 2001 {published data only}
-
- Mahalanabis D, Bhan MK. Micronutrients as adjunct therapy of acute illness in children: Impact on the episode outcome and policy implications of current findings. British Journal of Nutrition 2001;85(Suppl):151‐8. - PubMed
Qin 1999 {published data only}
-
- Qin XL. Observation of vitamin A as an adjuvant in the treatment of infant pneumonia. Jounral of Guangxi Medical University 1999;16(4):492‐3.
Quinlan 1996 {published data only}
-
- Quinlan K, Hayani K. Vitamin A and Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection.Serum levels and supplementation trial. Archives of Pediatric and Adolescent Medicine 1996;150:25‐30. - PubMed
Rahman 2001 {published data only}
Rahmathullah 1991 {published data only}
-
- Rahmathullah L, Underwood BA, Thulasiraj RD, Milton RC. Diarrhea, respiratory infections, and growth are not affected by a weekly low‐dose vitamin A supplement: a masked, controlled field trial in children in southern India. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1991;54:568‐77. - PubMed
Ramakrishnan 1998 {published data only}
-
- Ramakrishnan U, Martorell R. The role of vitamin A in reducing child mortality and morbidity and improving growth. Salud Publica de Mexico 1998;40:189‐98. - PubMed
Roy 1997 {published data only}
-
- Roy SK, Islam A, Molla A, Akramuzzaman SM, Jahan F, Fuchs G. Impact of a single megadose of vitamin A at delivery on breastmilk of mothers and morbidity of their infants. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1997;51:302‐7. - PubMed
Ruz 1995 {published data only}
-
- Ruz M, Solomons NW, Mejia LA, Chew F. Alteration of circulating micronutrients with overt and occult infections in anaemic Guatemalan preschool children. International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition 1995;46:257‐65. - PubMed
Semba 1993 {published data only}
-
- Semba RD, Graham NM, Caiaffa WT, Margolick JB, Clement L, Vlahov D. Increased mortality associated with vitamin A deficiency during human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. Archives of Internal Medicine 1993;153:2149‐54. - PubMed
Semba 1995 {published data only}
-
- Semba RD, Caiaffa WT, Graham NM, Cohn S, Vlahov D. Vitamin A deficiency and wasting as predictors of mortality in human immunodeficiency virus‐infected injection drug users. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1995;171:1196‐202. - PubMed
Semba 1999 {published data only}
-
- Semba RD. Vitamin A and immunity to viral, bacterial and protozoan infections. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society 1999;58:719‐27. - PubMed
Sempertegui 1999 {published data only}
-
- Sempertegui F, Estrella B, Camaniero V, Betancourt V, Izurieta R, Ortiz W, et al. The beneficial effects of weekly low‐dose vitamin A supplementation on acute lower respiratory infections and diarrhea in Ecuadorian children. Pediatrics 1999;104:e1. - PubMed
Shah 1994 {published data only}
-
- Shah N, Ramankutty V, Premila PG, Sathy N. Risk factors for severe pneumonia in children in south Kerala: a hospital‐based case‐control study. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics 1994;40:201‐6. - PubMed
Si 1997 {published data only}
-
- Si NV, Grytter C, Vy NN, Hue NB, Pedersen FK. High dose vitamin A supplementation in the course of pneumonia in Vietnamese children. Acta Paediatrica 1997;86:1052‐5. - PubMed
Stansfield 1993 {published data only}
-
- Stansfield SK, Pierre‐Louis M, Lerebours G, Augustin A. Vitamin A supplementation and increased prevalence of childhood diarrhoea and acute respiratory infections. Lancet 1993;342:578‐82. - PubMed
Stephensen 2002 {published data only}
-
- Stephensen CB, Franchi LM, Hernandez H, Campos M, Colarossi A, Gilman RH, et al. Assessment of vitamin A status with the relative dose response test in Peruvian children recovering from pneumonia. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2002;76:1351‐7. - PubMed
Tomkins 2000 {published data only}
-
- Tomkins A. Malnutrition, morbidity and mortality in children and their mothers. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society 2000;59:135‐46. - PubMed
Velasquez 1995 {published data only}
-
- Velasquez‐Melendez G, Okani ET, Kiertsman B, Roncada MJ. Vitamin A status in children with pneumonia. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1995;49:379‐84. - PubMed
Vijayaraghavan 1990 {published data only}
-
- Vijayaraghavan K, Radhaiah G, Prakasam BS, Sarma KV, Reddy V. Effect of massive dose vitamin A on morbidity and mortality in Indian children. Lancet 1990;336:1342‐5. - PubMed
Villamor 2000a {published data only}
-
- Villamor E, Fawzi WW. Vitamin A supplementation: implications for morbidity and mortality in children. Journal of Infectious Diseases 2000;182(Suppl):122‐33. - PubMed
Villamor 2000b {published data only}
-
- Villamor E, Mbise R, Spiegelman D, Ndossi G, Fawzi WW. Vitamin A supplementation and other predictors of anemia among children from Dar Es Salaam, Tanzania. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2000;62:590‐7. - PubMed
Wang 2003a {published data only}
-
- Wang W, Xie S. Vitamin A as an adjuvant in the treatment of persistent pneumonia. Herald of Medicine 2003;22(4):258‐9.
Wang 2003b {published data only}
-
- Wang W, Xie S. Vitamin A as an adjuvant in the treatment of persistent pneumonia. Journal of Nanhua University (Medical Edition) 2003;31(1):103‐4.
West 1991 {published data only}
-
- West KP Jr, Pokhrel RP, Katz J, LeClerq SC, Khatry SK, Shrestha SR, et al. Efficacy of vitamin A in reducing preschool child mortality in Nepal. Lancet 1991;338:67‐71. - PubMed
Willumsen 1997 {published data only}
-
- Willumsen JF, Simmank K, Filteau SM, Wagstaff LA, Tomkins AM. Toxic damage to the respiratory epithelium induces acute phase changes in vitamin A metabolism without depleting retinol stores of South African children. Journal of Nutrition 1997;127:1339‐43. - PubMed
Winkler 2005 {published data only}
-
- Winkler P, Vrese M, Laue C, Schrezenmeir J. Effect of a dietary supplement containing probiotic bacteria plus vitamins and minerals on common cold infections and cellular immune parameters. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2005;43(7):318‐26. [MEDLINE: ; ISSN: 0946‐1965] - PubMed
Wu 2000 {published data only}
-
- Wu Y. Effect observation of Vitamin A, Vitamin E as an adjuvant in the treatment of bronchopneumonia. Heilongjiang Medicine and Pharmacy 2000;23(4):25‐6.
Yang 2002 {published data only}
-
- Yang LL, Jia J. Effect of vitamin A as adjuvant drug in the treatment of pneumonia. Journal of Changzhi Medical College 2002;16(2):139‐40.
Ying 1998 {published data only}
-
- Ying GY. Effect of vitamin A in the treatment of pneumonia. Journal of Shanxi Medical University 1998;29(3):262‐3.
Zhen 2003 {published data only}
-
- Zhen B. Effect analysis of vitamin A as a complementary agent in the treatment of new born baby infectious pneumonia. Journal of Pediatric Pharmacy 2003;9(1):48‐9.
Additional references
Boissel 1989
-
- Boissel JP, Blanchard J, Panak E, Peyrieux JC, Sacks H. Considerations for the meta‐analysis of randomised clinical trials. Summary of a panel discussion. Controlled Clinical Trials 1989;10:254‐81. - PubMed
Brown 2004
-
- Brown N, Roberts C. Vitamin A for acute respiratory infection in developing countries: a meta‐analysis. Acta Paediatrics 2004;93(11):1437‐42. - PubMed
Cochran 1954
-
- Cochran W. The combination of estimates from different experiments. Biometrics 1954;10:101‐29.
Ellison 1932
Fawzi 1993
-
- Fawzi WW, Chalmers TC, Herrera MG, Mosteller F. Vitamin A supplementation and child mortality, a meta‐analysis. Journal of the American Medical Association 1993;269:899‐903. - PubMed
Fleiss 1986
-
- Fleiss JL. Analysis of data from multi clinical trials. Controlled Clinical Trials 1986;7:267‐75. - PubMed
Glasziou 1993
Julian 2009
-
- Julian PT Higgins, Douglas G Altman. Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Julian PT Higgins, Sally Green editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reivews of Interventions. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, September 2009.
Kirkwood 1995
Lefebvre 2009
-
- Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: Searching for studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.0.2 (updated September 2009). The Cochrane Collaboration. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org. Chichester, UK: Wiley‐Blackwell, 2009.
RevMan 2008 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre. The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2008.
Ross 1996
-
- Ross A. In: Sommer A, West K editor(s). Vitamin A deficiency: health, survival and vision. New York: Oxford University Press, 1996:251‐73.
Rundan 2004
-
- Rudan I, Tomaskovic L, Boschi‐Pinto C, Campbell H (on behalf of WHO Child Health Epidemiology Reference Group). Bulletin of the World Health Organization (Print ISSN 0042‐9686): Global estimate of the incidence of clinical pneumonia among children under five years of age. http://www.scielosp.org/scielo.php?pid=S0042‐96862004001200005&scrip... (accessed 30 March 2005). - PMC - PubMed
VAPWG 1995
-
- The Vitamin A and Pneumonia Working Group. Potential interventions for the prevention of childhood pneumonia in developing countries: a meta‐analysis of data from field trials to assess the impact of vitamin A supplementation on pneumonia morbidity and mortality. Bulletin of the World Health Organization 1995;73:609‐19. - PMC - PubMed
WHO 2010
-
- World Health Organization. Micronutrient deficiencies: Vitamin A deficiency. http://www.who.int/nutrition/topics/vad/en/ (Accessed 10 July 2010) 2010.
Yang 2009
-
- Yang HM, Mao M, Wan CM. Vitamin A for treating measles in children. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2009, Issue 3. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001479.pub3] - DOI
References to other published versions of this review
Ni 2005
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

