Rubber band ligation versus excisional haemorrhoidectomy for haemorrhoids
- PMID: 16034963
- PMCID: PMC8860341
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD005034.pub2
Rubber band ligation versus excisional haemorrhoidectomy for haemorrhoids
Abstract
Background: Traditional treatment methods for haemorrhoids fall into two broad groups: less invasive techniques including rubber band ligation (RBL), which tend to produce minimal pain, and the more radical techniques like excisional haemorrhoidectomy (EH), which are inherently more painful. For decades, innovations in the field of haemorrhoidal treatment have centred on modifying the traditional methods to achieve a minimally invasive, less painful procedure and yet with a more sustainable result. The availability of newer techniques has reopened debate on the roles of traditional treatment options for haemorrhoids.
Objectives: To review the efficacy and safety of the two most popular conventional methods of haemorrhoidal treatment, rubber band ligation and excisional haemorrhoidectomy.
Search strategy: We searched all the major electronic databases (MEDLINE, EMBASE, CENTRAL, CINAHL).
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials comparing rubber band ligation with excisional haemorrhoidectomy for symptomatic haemorrhoids in adult human patients were included.
Data collection and analysis: We extracted data on to previously designed data extraction sheet. Dichtomous data were presented as relative risk and 95% confidence intervals, and continuous outcomes as weighted mean difference and 95% confidence intervals.
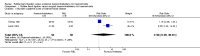
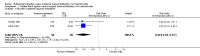
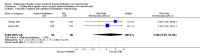
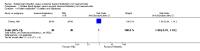
Main results: Three trials (of poor methodological quality) met the inclusion criteria. Complete remission of haemorrhoidal symptom was better with EH (three studies, 202 patients, RR 1.68, 95% CI 1.00 to 2.83). There was significant heterogeneity between the studies (I2 = 90.5%; P = 0.0001). Similar analysis based on the grading of haemorrhoids revealed the superiority of EH over RBL for grade III haemorrhoids (prolapse that needs manual reduction) (two trials, 116 patients, RR 1.23, CI 1.04 to 1.45; P = 0.01). However, no significant difference was noticed in grade II haemorrhoids (prolapse that reduces spontaneously on cessation of straining) (one trial, 32 patients, RR 1.07, CI 0.94 to 1.21; P = 0.32) Fewer patients required re-treatment after EH (three trials, RR 0.20 CI 0.09 to 0.40; P < 0.00001). Patients undergoing EH were at significantly higher risk of postoperative pain (three trials, fixed effect; 212 patients, RR 1.94, 95% CI 1.62 to 2.33, P < 0.00001). The overall delayed complication rate showed significant difference (P = 0.03) (three trials, 204 patients, RR 6.32, CI 1.15 to 34.89) between the two interventions.
Authors' conclusions: The present systematic review confirms the long-term efficacy of EH, at least for grade III haemorrhoids, compared to the less invasive technique of RBL but at the expense of increased pain, higher complications and more time off work. However, despite these disadvantages of EH, patient satisfaction and patient's acceptance of the treatment modalities seems to be similar following both the techniques implying patient's preference for complete long-term cure of symptoms and possibly less concern for minor complications. So, RBL can be adopted as the choice of treatment for grade II haemorrhoids with similar results but with out the side effects of EH while reserving EH for grade III haemorrhoids or recurrence after RBL. More robust study is required to make definitive conclusions.
Conflict of interest statement
None known
Figures








Comment in
-
Comments to 'Rubber band ligation versus excisional haemorrhoidectomy for haemorrhoids'.Tech Coloproctol. 2016 Sep;20(9):659-61. doi: 10.1007/s10151-016-1461-3. Epub 2016 Mar 29. Tech Coloproctol. 2016. PMID: 27023348
References
References to studies included in this review
Cheng 1981 {published data only}
-
- Cheng FCY, Shum DWP, Ong GB. The treatment of second degree haemorrhoids by injection, rubber band ligation, maximal anal dilatation, and haemorrhoidectomy: a prospective clinical trial. Australian and New Zealand journal of surgery 1981;51(5):458‐62. - PubMed
Lewis 1983 {published data only}
-
- Lewis AAM, ROGERS HS, Leighton M. Trial of maximal anal dilatation, cryotherapy and elastic band ligation as alternatives to haemorrhoidectomy in the treatment of large prolapsing haemorrhoids. British Journal of Surgery 1983;70:54‐56. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Murie 1980 {published data only}
-
- Murie JA, Mackenzie I, Sim AJW. Comparison of rubber band ligation and haemorrhoidectomy for second‐ and third‐degree haemorrhoids: A prospective clinical trial. British Journal of Surgery 1980;67(11):786‐788. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Adekunle 1984 {published data only}
-
- Adekunle OO, Kolawole JF. A comparative study of excisional surgery and cryohaemorrhoidectomy. African Journal of Medicine & Medical Sciences 1984;13(1‐2):7‐13. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ali 2005 {published data only}
-
- Ali U, Khan AS. Rubber Band Ligation versus Open Haemorrhoidectomy: A study of 100 cases. Journal of Postgraduate Medical Institute 2005;19(3):31 7‐22.
Ambrose 1983 {published data only}
Arabi 1977 {published data only}
-
- Arabi Y, Gatehouse D, Alexander‐Williams J, Keighley MR. Rubber band ligation or lateral subcutaneous sphincterotomy for the treatment of haemorrhoids. British Journal of Surgery 1977;64(10):737‐40. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Carapeti 1998 {published data only}
-
- Carapeti EA, Kamm MA, McDonald PJ, Phillips RK. Double‐blind randomised controlled trial of effect of metronidazole on pain after day‐case haemorrhoidectomy. Lancet 1998;351(9097):169‐72. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Filingeri 2004 {published data only}
-
- Filingeri V, Gravante G, Baldessari E, Grimaldi M, Casciani CU. Prospective randomised trial of submucosal haemorrhoidectomy with radiofrequency bistoury vs. conventional Park's operation. Techniques in Coloproctology 2004;8(1):31‐6. - PubMed
Forster 1996 {published data only}
-
- Froster CF, Sussmann HE, Patzelt‐Wenczler R. Optimization of the Barron ligature treatment of 2nd and 3rd‐degree haemorrhoids using a therapeutic troika. Schweizerische Rundschau fur Medizin Praxis 1996;85(46):1476‐81. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gartell 1985 {published data only}
-
- Gartell PC, Sheridan RJ, McGinn FP. Out‐patient treatment of haemorrhoids: a randomized trial to compare rubber band ligation with phenol injection. British Journal of Surgery 1985;72(6):478‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Griffith 1987 {published data only}
-
- Griffith CDM, Morris DL, Wherry DC, Hardcastle JD. Out patient treatment of haemorrhoids: a randomised trial comparing contact bipolar diathermy with rubber band ligation. Coloproctology 1987;6:332‐334.
Hardy 1975 {published data only}
-
- Hardy KJ, Wheatley IC, Heffernan EB. Anal dilatation and haemorrhoidectomy. A prospective study. Medical Journal of Australia 1975;2(3):88‐91. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hiltunen 1992 {published data only}
-
- Hiltunen KM, Matikainen M. Anal dilatation, lateral subcutaneous sphincterotomy and haemorrhoidectomy for the treatment of second and third degree haemorrhoids. A prospective randomized study. International Surgery 1992;77(4):261‐3. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jones 1974 {published data only}
Keighley 1979 {published data only}
Lacerda‐Filho 1997 {published data only}
-
- Lacerda‐Filho A, Cunha‐Melo JR. Outpatient haemorrhoidectomy under local anaesthesia. European Journal of Surgery 1997;163(12):935‐40. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
MacRae 1995 {published data only}
-
- MacRae HM, McLeod RS. Comparison of Hemorrhoidal Treatment Modalities. A meta‐analysis. Dis Colon Rectum 1995;38(7):687‐94. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Murie 1982 {published data only}
-
- Murie JA, Sim AJ, Mackenzie I. Rubber band ligation versus haemorrhoidectomy for prolapsing haemorrhoids: a long term prospective clinical trial. British Journal of Surgery 1982;69(9):536‐38. - PubMed
Narro 2004 {published data only}
-
- Narro JL. Haemorrhoid therapy with doppler guided haemorrhoidal artery ligation via proctoscope KM‐25. A new alternative to haemorrhoidectomy and rubber band ligation?. Zentralblatt fur Chirurgie 2004;129(3):208‐210. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
O'Callaghan 1982 {published data only}
-
- O'Callaghan JD, Matheson TS, Hall R. Inpatient treatment of prolapsing piles: cryosurgery versus Milligan‐Morgan haemorrhoidectomy.. British Journal of Surgery 1982;69(3):157‐9. - PubMed
Rasmussen 1991 {published data only}
-
- Rasmussen O, Larsen KGL, Naver L, Christiansen J. Emergency haemorrhoidectomy compared with incision and banding for the treatment of acute strangulated haemorrhoids: A prospective randomised study. European Journal of Surgery 1991;157:613‐614. - PubMed
Read 1982 {published data only}
-
- Read MG, Read NW, Haynes WG, Donnelly TC, Johnson AG. A prospective study of the effect of haemorrhoidectomy on sphincter function and faecal continence. British Journal of Surgery 1982;69(7):396‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Seow‐Choen 1992 {published data only}
-
- Seow‐Choen F, Ho YH, Ang HG, Goh HS. Prospective, randomized trial comparing pain and clinical function after conventional scissors excision/ligation vs. diathermy excision without ligation for symptomatic prolapsed hemorrhoids. Diseases of the colon and rectum 1992;35(12):1165‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sim 1981 {published data only}
-
- Sim AJ, Murie JA, Mackenzie I. Comparison of rubber band ligation and sclerosant injection for first and second degree haemorrhoids‐ a prospective clinical trial. Acta Chirurgica Scandinavica 1981;147(8):717‐20. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Templeton 1983 {published data only}
-
- Templeton JL, Spence RA, Kennedy TL, Parks AG, Mackenzie G, Hanna WA. Comparison of infrared coagulation and rubber band ligation for first and second degree haemorrhoids: a randomised prospective clinical trial. British Medical Journal Clinical Research Ed.. 1983;286(6375):1387‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
Wehrmann 2004 {published data only}
-
- Wehrmann T, Riphaus A, Feinstein J, Stergiou N. Hemorrhoidal elastic band ligation with flexible videoendoscopes: a prospective, randomized comparison with the conventional technique that uses rigid proctoscopes.. Gastrointestinal endoscopy 2004;60(2):191‐5. - PubMed
Additional references
Barron 1963
-
- Barron J. Office ligation of internal hemorrhoids. American journal of Surgery 1963;105(4):563‐570. - PubMed
Barwell 1999
-
- Barwell J, Watkins RM, Lloyd‐Davies E, Wilkins DC. Life‐Threatening Retroperitoneal Sepsis After Hemorrhois Injection Sclerotherapy. Report of a case. Diseases of the colon and rectum 1999;42(3):421‐23. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bat 1993
-
- Bat L, Melzer E, Koler M, Dreznick Z. Complications of Rubber Band Ligation of Symptomatic Internal Hemorrhoids. Diseases of the colon and rectum 1993;36(3):287‐290. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Blaisdell 1958
-
- Blaisdell PC. Office ligation of internal hemorrhoids. American journal of Surgery 1958;96(3):401‐404. - PubMed
Bleday 1992
-
- Bleday R, Pena JP, Rothenberger DA, Goldberg SM, Buls JG. Symptomatic Hemorrhoids: Current Incidence and Complications of Operative Therapy. Diseases of the colon and rectum 1992;35(5):477‐481. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Brisinda 2000
Der Simonian 1986
-
- Simonian R, Laird N. Meta‐analysis in clinical trials. Controlled clinical trials 1986;7:177‐88. - PubMed
Goligher 1984
-
- Goligher J, Duthie H, Nixon H. Surgery of the Anus Rectum and Colon. 5. London: Baillière Tindall, 1984.
Haas 1984
-
- Haas PA, Fox TA Jr, Haas GP. The Pathogenesis of haemorrhoids. Diseases of the colon and rectum 1984;27(7):442‐50. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Johanson 1990
-
- Johanson JF, Sonnenberg A. The prevalence of haemorrhoids and chronic constipation: an epidemiological study. Gastroenterology 1990;98(2):380‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Keighley 1993
-
- Keighley MRB. Surgery of Anus, Rectum and Colon. 1. Vol. 1, WB Saunders publishers, 1993:295‐8.
Lehnhardt 2004
-
- Lehnhardt M, Steinstrauesser L, Drueke D, Muehlberger T, Steinau HU, Homann HH. Fournier's gangrene after Milligan‐Morgan haemorrhoidectomy requiring subsequent abdominoperineal resection of the rectum: report of a case. Diseases of the colon and rectum 2004;47(10):1729‐33. - PubMed
Longo 1998
-
- Longo A. Treatment of Hemorrhoid Disease by Reduction in Mucosal and Haemorrhoidal Products with a Circular Stapling Device ‐ New Procedure.. Proceedings of the 6th World Congress of Endoscopic Surgery, Rome, Italy. Rome, Italy, 1998.
Manson 2002
-
- Monson JRT, Mortenson NJ, Hartley J. Procedures for Prolapsing Haemorrhoids (PPH) or Stapled Anopexy. Consensus Document for Association of Coloproctology of Great Britain and Ireland. ACPGBI, 2003.
Nisar 2003
Parks 1955
-
- Parks AG. De Haemorrhois. A study in surgical history. Guy's Hospital report 1955;104:135‐50. - PubMed
Rogozina 2002
-
- Rogozina VA. Hemorrhoids. Eksperimental'Naia i Klinicheskaia Gastroenterologiia 2002;4:93‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sardinha 2002
-
- Sardinha TC, Corman ML. Haemorrhoids. The Surgical clinics of North America 2002; Vol. 82, issue 6:1153‐67. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Thaha 2002
-
- Thaha MA, Campbell KL, Steele RJC. Non‐operative treatment for haemorrhoidal disease. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2002, Issue 3. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003771] - DOI
Thomson 1975
-
- Thomson WHF. The nature of Haemorrhoids. British Journal of Surgery 1975;62(7):542‐52. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

