C-terminus of heat shock protein 70-interacting protein facilitates degradation of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 and inhibits apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1-dependent apoptosis
- PMID: 16038411
- PMCID: PMC1176473
- DOI: 10.1379/csc-90r.1
C-terminus of heat shock protein 70-interacting protein facilitates degradation of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 and inhibits apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1-dependent apoptosis
Abstract
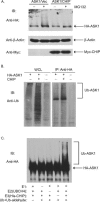
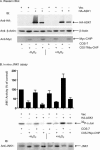
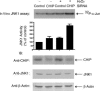
Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) is a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase (MAPKKK) that is regulated under conditions of cellular stress. ASK1 phosphorylates c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and elicits an apoptotic response. ASK1 activity is regulated at multiple levels, 1 of which is through inhibition by cytosolic chaperones of the heat shock protein (Hsp) 70 family. Among the proteins that determine Hsp70 function, CHIP (C-terminus of Hsp70-interacting protein) is a cochaperone and ubiquitin ligase that interacts with Hsp70 through an amino-terminal tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR) domain. Prominent among the cellular functions mediated by CHIP is protection against physiologic stress. Because ASK1 is known to contain a TPR-acceptor site, we examined the role of CHIP in regulating ASK1 function. CHIP interacted with ASK1 in a TPR-dependent fashion and induced ubiquitylation and proteasome-dependent degradation of ASK1. Targeting of ASK1 by CHIP inhibited JNK activation in response to oxidative challenge and reduced ASK1-dependent apoptosis, whereas short interfering RNA (siRNA)-dependent depletion of CHIP enhanced JNK activation. Consistent with its ability to reduce cytoplasmic ASK1 levels, CHIP triggered the translocation of ASK1 partner protein death-associated protein (Daxx) into the nucleus, where it is known to activate an antiapoptotic response. These results indicate that CHIP regulates ASK1 activity by inducing its ubiquitylation and degradation, which, together with its effects on Daxx localization, provides a mechanism for the antiapoptotic effects of CHIP observed in the face of cellular and physiologic stress.
Figures

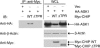

Similar articles
-
Heat shock protein 70 together with its co-chaperone CHIP inhibits TNF-alpha induced apoptosis by promoting proteasomal degradation of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase1.Apoptosis. 2010 Jul;15(7):822-33. doi: 10.1007/s10495-010-0495-7. Apoptosis. 2010. PMID: 20349136
-
beta-Arrestins facilitate ubiquitin-dependent degradation of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) and attenuate H2O2-induced apoptosis.Cell Signal. 2009 Jul;21(7):1195-206. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2009.03.010. Epub 2009 Mar 21. Cell Signal. 2009. PMID: 19306926
-
β-TrCP-dependent degradation of ASK1 suppresses the induction of the apoptotic response by oxidative stress.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2018 Oct;1862(10):2271-2280. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2018.07.015. Epub 2018 Jul 18. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2018. PMID: 30031111
-
[Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Signaling: Regulatory Mechanisms and Pathophysiological Roles].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019;139(10):1235-1241. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.19-00141. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019. PMID: 31582606 Review. Japanese.
-
Physiological roles of ASK1-mediated signal transduction in oxidative stress- and endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis: advanced findings from ASK1 knockout mice.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2002 Jun;4(3):415-25. doi: 10.1089/15230860260196218. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2002. PMID: 12215209 Review.
Cited by
-
CHIP-mediated CIB1 ubiquitination regulated epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma.Cell Death Differ. 2021 Mar;28(3):1026-1040. doi: 10.1038/s41418-020-00635-5. Epub 2020 Oct 20. Cell Death Differ. 2021. PMID: 33082516 Free PMC article.
-
Implication of 14-3-3ε and 14-3-3θ/τ in proteasome inhibition-induced apoptosis of glioma cells.Cancer Sci. 2013 Jan;104(1):55-61. doi: 10.1111/cas.12033. Epub 2012 Nov 28. Cancer Sci. 2013. PMID: 23020756 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying the substrate proteins of U-box E3s E4B and CHIP by orthogonal ubiquitin transfer.Sci Adv. 2018 Jan 3;4(1):e1701393. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1701393. eCollection 2018 Jan. Sci Adv. 2018. PMID: 29326975 Free PMC article.
-
C terminus of Hsc70-interacting protein promotes smooth muscle cell proliferation and survival through ubiquitin-mediated degradation of FoxO1.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jul 24;284(30):20090-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.017046. Epub 2009 May 29. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19483080 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting ASK1 signaling in neurodegeneration: molecular insights and therapeutic promise.Apoptosis. 2025 Jul 23. doi: 10.1007/s10495-025-02148-3. Online ahead of print. Apoptosis. 2025. PMID: 40702249 Review.
References
-
- Ballinger CA, Connell P, Wu Y, Hu Z, Thompson LJ, Yin L-Y, Patterson C. Identification of CHIP, a novel tetratricopeptide repeat-containing protein that interacts with heat shock proteins and negatively regulates chaperone functions. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:4535–4545.0270-7306(1999)019[4535:IOCANT]2.0.CO;2 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beere HM, Wolf BB, and Cain K. et al. 2000 Heat-shock protein 70 inhibits apoptosis by preventing recruitment of procaspase-9 to the Apaf-1 apoptosome. Nat Cell Biol. 2:469–475. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
