Heparin stimulates Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation
- PMID: 16040971
- PMCID: PMC1201187
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.73.8.4596-4606.2005
Heparin stimulates Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation
Abstract
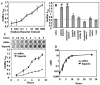
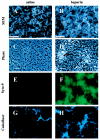
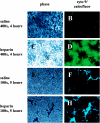
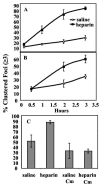
Heparin, known for its anticoagulant activity, is commonly used in catheter locks. Staphylococcus aureus, a versatile human and animal pathogen, is commonly associated with catheter-related bloodstream infections and has evolved a number of mechanisms through which it adheres to biotic and abiotic surfaces. We demonstrate that heparin increased biofilm formation by several S. aureus strains. Surface coverage and the kinetics of biofilm formation were stimulated, but primary attachment to the surface was not affected. Heparin increased S. aureus cell-cell interactions in a protein synthesis-dependent manner. The addition of heparin rescued biofilm formation of hla, ica, and sarA mutants. Our data further suggest that heparin stimulation of biofilm formation occurs neither through an increase in sigB activity nor through an increase in polysaccharide intracellular adhesin levels. These finding suggests that heparin stimulates S. aureus biofilm formation via a novel pathway.
Figures
References
-
- Arnow, P. M., E. M. Quimosing, and M. Beach. 1993. Consequences of intravascular catheter sepsis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 16:778-784. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

