Computational tradeoffs in multiplex PCR assay design for SNP genotyping
- PMID: 16042802
- PMCID: PMC1190169
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-6-102
Computational tradeoffs in multiplex PCR assay design for SNP genotyping
Abstract
Background: Multiplex PCR is a key technology for detecting infectious microorganisms, whole-genome sequencing, forensic analysis, and for enabling flexible yet low-cost genotyping. However, the design of a multiplex PCR assays requires the consideration of multiple competing objectives and physical constraints, and extensive computational analysis must be performed in order to identify the possible formation of primer-dimers that can negatively impact product yield.
Results: This paper examines the computational design limits of multiplex PCR in the context of SNP genotyping and examines tradeoffs associated with several key design factors including multiplexing level (the number of primer pairs per tube), coverage (the % of SNP whose associated primers are actually assigned to one of several available tube), and tube-size uniformity. We also examine how design performance depends on the total number of available SNPs from which to choose, and primer stringency criterial. We show that finding high-multiplexing/high-coverage designs is subject to a computational phase transition, becoming dramatically more difficult when the probability of primer pair interaction exceeds a critical threshold. The precise location of this critical transition point depends on the number of available SNPs and the level of multiplexing required. We also demonstrate how coverage performance is impacted by the number of available snps, primer selection criteria, and target multiplexing levels.
Conclusion: The presence of a phase transition suggests limits to scaling Multiplex PCR performance for high-throughput genomics applications. Achieving broad SNP coverage rapidly transitions from being very easy to very hard as the target multiplexing level (# of primer pairs per tube) increases. The onset of a phase transition can be "delayed" by having a larger pool of SNPs, or loosening primer selection constraints so as to increase the number of candidate primer pairs per SNP, though the latter may produce other adverse effects. The resulting design performance tradeoffs define a benchmark that can serve as the basis for comparing competing multiplex PCR design optimization algorithms and can also provide general rules-of-thumb to experimentalists seeking to understand the performance limits of standard multiplex PCR.
Figures
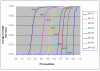
 . Full-tube coverage, the percentage of SNPs assigned to full tubes, of close to 80% is achieved at a multiplexing level of 20, though it drops rapidly for higher multiplexing levels. The graph shows a significant improvement in one algorithm over the other, demonstrating that such tradeoffs can be used to effectively compare and contrast competing optimization strategies.
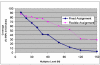
. Full-tube coverage, the percentage of SNPs assigned to full tubes, of close to 80% is achieved at a multiplexing level of 20, though it drops rapidly for higher multiplexing levels. The graph shows a significant improvement in one algorithm over the other, demonstrating that such tradeoffs can be used to effectively compare and contrast competing optimization strategies.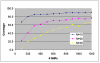
 = 34 tubes. Since M does not divide N evenly, the algorithm ends up partially filling the excess tube rather than working harder to fill the remaining 33 tubes to full 30-plex capacity.
= 34 tubes. Since M does not divide N evenly, the algorithm ends up partially filling the excess tube rather than working harder to fill the remaining 33 tubes to full 30-plex capacity.
References
-
- Gibson UE, Heid CA, Williams PM. A novel method for real time quantitative RT-PCR. Genome Res. 1996;6:995–1001. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

