HIV-1 Nef down-regulates the hemochromatosis protein HFE, manipulating cellular iron homeostasis
- PMID: 16043695
- PMCID: PMC1180511
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0504823102
HIV-1 Nef down-regulates the hemochromatosis protein HFE, manipulating cellular iron homeostasis
Abstract
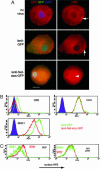
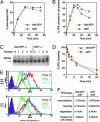
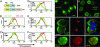
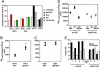
The multifunctional Nef protein of HIV-1 is important for the progression to AIDS. One action of Nef is to down-regulate surface MHC I molecules, helping infected cells to evade immunity. We found that Nef also down-regulates the macrophage-expressed MHC 1b protein HFE, which regulates iron homeostasis and is mutated in the iron-overloading disorder hemochromatosis. In model cell lines, Nef reroutes HFE to a perinuclear structure that overlaps the trans-Golgi network, causing a 90% reduction of surface HFE. This activity requires a Src-kinase-binding proline-rich domain of Nef and a conserved tyrosine-based motif in the cytoplasmic tail of HFE. HIV-1 infection of ex vivo macrophages similarly down-regulates naturally expressed surface HFE in a Nef-dependent manner. The effect of Nef expression on cellular iron was explored; iron and ferritin accumulation were increased in HIV-1-infected ex vivo macrophages expressing wild-type HFE, but this effect was lost with Nef-deleted HIV-1 or when infecting macrophages from hemochromatosis patients expressing mutated HFE. The iron accumulation in HIV-1-infected HFE-expressing macrophages was paralleled by an increase in cellular HIV-1-gag expression. We conclude that, through Nef and HFE, HIV-1 directly regulates cellular iron metabolism, possibly benefiting viral growth.
Figures


References
-
- Deacon, N. J., Tsykin, A., Solomon, A., Smith, K., Ludford-Menting, M., Hooker, D. J., McPhee, D. A., Greenway, A. L., Ellett, A., Chatfield, C., et al. (1995) Science 270, 988-991. - PubMed
-
- She, H., Xiong, S., Lin, M., Zandi, E., Giulivi, C. & Tsukamoto, H. (2002) in Am. J. Physiol. 283, G719-G726. - PubMed
-
- Guy, B., Kieny, M. P., Riviere, Y., Le Peuch, C., Dott, K., Girard, M., Montagnier, L. & Lecocq, J. P. (1987) Nature 330, 266-269. - PubMed
-
- Aiken, C., Konner, J., Landau, N. R., Lenburg, M. E. & Trono, D. (1994) Cell 76, 853-864. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

