Detection of myelination using a novel histological probe
- PMID: 16046669
- PMCID: PMC3957546
- DOI: 10.1369/jhc.5A6704.2005
Detection of myelination using a novel histological probe
Abstract
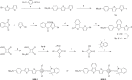
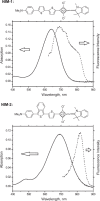
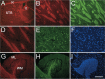
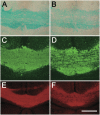
Current methods for myelin staining in tissue sections include both histological and immunohistochemical techniques. Fluorescence immunohistochemistry, which uses antibodies against myelin components such as myelin basic protein, is often used because of the convenience for multiple labeling. To facilitate studies on myelin, this paper describes a quick and easy method for direct myelin staining in rodent and human tissues using novel near-infrared myelin (NIM) dyes that are comparable to other well-characterized histochemical reagents. The near-infrared fluorescence spectra of these probes allow fluorescent staining of tissue sections in multiple channels using visible light fluorophores commonly used in immunocytochemistry. These dyes have been used successfully to detect normal myelin structure and myelin loss in a mouse model of demyelination disease.
Figures
References
-
- Hirano M, Osakada K, Nohira H, Miyashita A. (2002) Crystal and solution structures of photochromic spirobenzothiopyran. First full characterization of the meta-stable colored species. J Org Chem 67: 533–540 - PubMed
-
- Klüver H, Barrera E. (1953) A method for the combined staining of cells and fibers in the central nervous system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 12: 400–403 - PubMed
-
- Kuhn H, Schweig A. (1967) Theoretical treatment of solvent effects on the electronic spectra of polar organic dye molecules. Chem Phys Lett 1: 255–258
-
- Nakazumi H, Colyer C, Kaihara K, Yagi S, Hyodo Y. (2003) Red luminescent squarylium dyes for noncovalent HAS labeling. Chem Lett 32: 804–805
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

