Planar Tc99m--sestamibi scintimammography should be considered cautiously in the axillary evaluation of breast cancer protocols: results of an international multicenter trial
- PMID: 16048648
- PMCID: PMC1199526
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2385-5-4
Planar Tc99m--sestamibi scintimammography should be considered cautiously in the axillary evaluation of breast cancer protocols: results of an international multicenter trial
Abstract
Background: Lymph node status is the most important prognostic indicator in breast cancer in recently diagnosed primary lesion. As a part of an interregional protocol using scintimammography with Tc99m compounds, the value of planar Tc99m sestamibi scanning for axillary lymph node evaluation is presented. Since there is a wide range of reported values, a standardized protocol of planar imaging was performed.
Methods: One hundred and forty-nine female patients were included prospectively from different regions. Their mean age was 55.1 +/- 11.9 years. Histological report was obtained from 2.987 excised lymph nodes from 150 axillas. An early planar chest image was obtained at 10 min in all patients and a delayed one in 95 patients, all images performed with 740-925 MBq dose of Tc99m sestamibi. Blind lecture of all axillary regions was interpreted by 2 independent observers considering any well defined focal area of increased uptake as an involved axilla. Diagnostic values, 95% confidence intervals [CI] and also likelihood ratios (LR) were calculated.
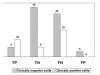
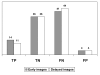
Results: Node histology demonstrated tumor involvement in 546 out of 2987 lymph nodes. Sestamibi was positive in 30 axillas (25 true-positive) and negative in 120 (only 55 true-negative). The sensitivity corresponded to 27.8% [CI = 18.9-38.2] and specificity to 91.7% [81.6-97.2]. The positive and negative LR were 3.33 and 0.79, respectively. There was no difference between early and delayed images. Sensitivity was higher in patients with palpable lesions.
Conclusion: This work confirmed that non tomographic Tc99m sestamibi scintimammography had a very low detection rate for axillary lymph node involvement and it should not be applied for clinical assessment of breast cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Technetium-99m-sestamibi prone scintimammography to detect primary breast cancer and axillary lymph node involvement.J Nucl Med. 1995 Oct;36(10):1758-65. J Nucl Med. 1995. PMID: 7562039
-
(99M)Technetium-sestamibi scintimammography in non-palpable breast lesions found on screening X-ray mammography.Eur J Surg Oncol. 2007 Feb;33(1):23-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2006.10.025. Epub 2006 Nov 27. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2007. PMID: 17126524
-
Metastatic axillary lymph node technetium-99m-MIBI imaging in primary breast cancer.J Nucl Med. 1998 Mar;39(3):459-64. J Nucl Med. 1998. PMID: 9529292
-
Use of tomographic nuclear medicine procedures, SPECT and pinhole SPECT, with cationic lipophilic radiotracers for the evaluation of axillary lymph node status in breast cancer patients.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2004 Jun;31 Suppl 1:S23-34. doi: 10.1007/s00259-004-1524-y. Epub 2004 Apr 15. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2004. PMID: 15085293 Review.
-
Sentinel lymph node as a new marker for therapeutic planning in breast cancer patients.J Surg Oncol. 2004 Mar;85(3):102-11. doi: 10.1002/jso.20022. J Surg Oncol. 2004. PMID: 14991881 Review.
Cited by
-
Breast imaging: A survey.World J Clin Oncol. 2011 Apr 10;2(4):171-8. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v2.i4.171. World J Clin Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21611093 Free PMC article.
-
Intrathyroidal parathyroid adenomas: Scoping review on clinical presentation, preoperative localization, and surgical treatment.Head Neck. 2023 Mar;45(3):706-720. doi: 10.1002/hed.27287. Epub 2022 Dec 23. Head Neck. 2023. PMID: 36563301 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bedrosian I, Bedi D, Kuerer HM, Fornage BD, Harker L, Ross MI, Ames FC, Krishnamurthy S, Edeiken-Monroe BS, Meric F, Feig BW, Akins J, Singletary SE, Mirza NQ, Hunt KK. Impact of clinicopathological factors on sensitivity of axillary ultrasonography in the detection of axillary nodal metastases in patients with breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2003;10:1025–30. doi: 10.1245/ASO.2003.12.017. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Buscombe JR, Holloway B, Roche N, Bombardieri E. Position of nuclear medicine modalities in the diagnostic work-up of breast cancer. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2004;48:109–18. - PubMed
-
- Greco M, Crippa F, Agresti R, Seregni E, Gerali A, Giovanazzi R, Micheli A, Asero S, Ferraris C, Gennaro M, Bombardieri E, Cascinelli N. Axillary lymph node staging in breast cancer by 2-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose-positron emission tomography: clinical evaluation and alternative management. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001;93:630–5. doi: 10.1093/jnci/93.8.630. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials