Off-trial evaluation of bisphosphonates in patients with metastatic breast cancer
- PMID: 16048654
- PMCID: PMC1184064
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-5-89
Off-trial evaluation of bisphosphonates in patients with metastatic breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Bisphosphonate therapy has been readily accepted as standard of care for individuals with bone metastases from breast cancer. In this study we determined whether the proportion of patients experiencing a skeletal related event (SRE) in a clinical practice population was similar to that observed in phase III randomized controlled studies.
Methods: A retrospective chart review was conducted of 110 patients receiving intravenous bisphosphonates for advanced breast cancer. The proportion of patients experiencing at least one SRE after 12 months of therapy was determined. SRE included vertebral or non-vertebral fracture, cord compression, surgery and/or radiotherapy to bone.
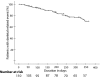
Results: The proportion of patients who had an SRE was 30% (28 individuals) and the median time to first event was greater than 350 days. Non-vertebral events and radiotherapy were the most frequent type of SRE, while cord compression and hypercalcaemia were rare (1%). Most patients in the study had bone-only disease (58.2%) and most had multiple bone lesions. In the first 12 months the mean duration of exposure to intravenous bisphosphonates was 261 days and most patients remained on treatment until just before death (median 27 days).
Conclusion: This study suggests that the rate of clinically relevant SREs is substantially lower than the event rate observed in phase III clinical trials. We attribute this lower rate to observational bias. In the clinical trial setting it is possible that over-detection of skeletal events occurs due to the utilisation of regular skeletal survey or radionucleotide bone scan, whereas these procedures are not routine in clinical practice. Phase IV observational studies need to be conducted to determine the true benefits of bisphosphonate therapy in order to implement rationale use of bisphosphonates.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of zoledronic acid in patients with breast cancer metastatic to bone: a multicenter clinical trial.Oncologist. 2006 Jul-Aug;11(7):841-8. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.11-7-841. Oncologist. 2006. PMID: 16880243 Clinical Trial.
-
Approval summary for zoledronic acid for treatment of multiple myeloma and cancer bone metastases.Clin Cancer Res. 2003 Jul;9(7):2394-9. Clin Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12855610 Clinical Trial.
-
Phase II trial evaluating the palliative benefit of second-line zoledronic acid in breast cancer patients with either a skeletal-related event or progressive bone metastases despite first-line bisphosphonate therapy.J Clin Oncol. 2006 Oct 20;24(30):4895-900. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.05.9212. Epub 2006 Sep 25. J Clin Oncol. 2006. PMID: 17001071 Clinical Trial.
-
Bisphosphonates for cancer patients: why, how, and when?Support Care Cancer. 2002 Jul;10(5):399-407. doi: 10.1007/s005200100292. Epub 2001 Oct 19. Support Care Cancer. 2002. PMID: 12136223 Review.
-
Recommendations for zoledronic acid treatment of patients with bone metastases.Oncologist. 2005 Jan;10(1):52-62. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.10-1-52. Oncologist. 2005. PMID: 15632252 Review.
Cited by
-
Skeletal-related events (SREs) in breast cancer patients with bone metastases treated in the nontrial setting.Support Care Cancer. 2010 Feb;18(2):197-203. doi: 10.1007/s00520-009-0645-z. Epub 2009 May 8. Support Care Cancer. 2010. PMID: 19424729
-
Symptomatic skeletal-related events in patients receiving longer term bone-modifying agents for bone metastases from breast and castration resistant prostate cancers.Support Care Cancer. 2022 May;30(5):3977-3984. doi: 10.1007/s00520-021-06714-8. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Support Care Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35059864 Clinical Trial.
-
Risk Factors for Developing Skeletal-Related Events in Breast Cancer Patients With Bone Metastases Undergoing Treatment With Bone-Modifying Agents.Oncologist. 2016 Apr;21(4):508-13. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2015-0377. Epub 2016 Mar 14. Oncologist. 2016. PMID: 26975863 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the results of bisphosphonate use in clinical trials with actual practice: a case of apples and oranges?Curr Oncol. 2006 Oct;13(5):187-90. doi: 10.3390/curroncol13050018. Curr Oncol. 2006. PMID: 22792016 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Incidence, consequences and treatment of bone metastases in breast cancer patients-Experience from a single cancer centre.J Bone Oncol. 2013 Oct 3;2(4):137-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jbo.2013.09.001. eCollection 2013 Dec. J Bone Oncol. 2013. PMID: 26909284 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hortobagyi GN, Theriault RL, Porter L, Blayney D, Lipton A, Sinoff C, Wheeler H, Simeone JF, Seaman J, Knight RD. Efficacy of pamidronate in reducing skeletal complications in patients with breast cancer and lytic bone metastases. Protocol 19 Aredia Breast Cancer Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1996;335:1785–1791. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199612123352401. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hortobagyi GN, Theriault RL, Lipton A, Porter L, Blayney D, Sinoff C, Wheeler H, Simeone JF, Seaman JJ, Knight RD, Heffernan M, Mellars K, Reitsma DJ. Long-term prevention of skeletal complications of metastatic breast cancer with pamidronate. Protocol 19 Aredia Breast Cancer Study Group. J Clin Oncol. 1998;16:2038–2044. - PubMed
-
- Theriault RL, Lipton A, Hortobagyi GN, Leff R, Gluck S, Stewart JF, Costello S, Kennedy I, Simeone J, Seaman JJ, Knight RD, Mellars K, Heffernan M, Reitsma DJ. Pamidronate reduces skeletal morbidity in women with advanced breast cancer and lytic bone lesions: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Protocol 18 Aredia Breast Cancer Study Group. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:846–854. - PubMed
-
- Rosen LS, Gordon D, Kaminski M, Howell A, Belch A, Mackey J, Apffelstaedt J, Hussein M, Coleman RE, Reitsma DJ, Seaman JJ, Chen BL, Ambros Y. Zoledronic acid versus pamidronate in the treatment of skeletal metastases in patients with breast cancer or osteolytic lesions of multiple myeloma: a phase III, double-blind, comparative trial. Cancer J. 2001;7:377–387. - PubMed
-
- Rosen LS, Gordon D, Kaminski M, Howell A, Belch A, Mackey J, Apffelstaedt J, Hussein MA, Coleman RE, Reitsma DJ, Chen BL, Seaman JJ. Long-term efficacy and safety of zoledronic acid compared with pamidronate disodium in the treatment of skeletal complications in patients with advanced multiple myeloma or breast carcinoma: a randomized, double-blind, multicenter, comparative trial. Cancer. 2003;98:1735–1744. doi: 10.1002/cncr.11701. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical