Efficacy of Telavancin in a rabbit model of aortic valve endocarditis due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus or vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 16048918
- PMCID: PMC1196289
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.49.8.3163-3165.2005
Efficacy of Telavancin in a rabbit model of aortic valve endocarditis due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus or vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
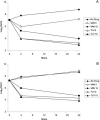
The activities of telavancin and vancomycin were compared in vitro and in the rabbit model of aortic valve endocarditis against a methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strain, COL, and a vancomycin-intermediate S. aureus (VISA) strain, HIP 5836. Telavancin was bactericidal in time-kill studies at a concentration of 5 microg/ml against both COL and HIP5836. Vancomycin was bacteriostatic at 5 microg/ml and bactericidal at 10 microg/ml against COL and was bacteriostatic at 10 microg/ml against VISA strain HIP 5836. Compared to untreated controls, a twice-daily regimen of 30 mg/kg of telavancin reduced mean aortic valve vegetation titers of the COL strain by 4.7 log(10) CFU/g after 4 days of therapy and sterilized 6/11 vegetations compared to 3.4 log(10) CFU/g with 3/10 vegetations sterilized for a regimen of twice-daily vancomycin, 30 mg/kg; these differences were not statistically significant. Telavancin was significantly more effective than vancomycin in the VISA model, producing a 5.5 log(10) CFU/g reduction versus no reduction in CFU with vancomycin. In experiments comparing 2-day regimens of telavancin at 30 mg/kg and 50 mg/kg twice daily, organisms were rapidly eliminated from vegetations, but the effect was not different between the two doses. These results suggest that telavancin may be an effective treatment for endocarditis and other serious staphylococcal infections accompanied by bacteremia, including infections caused by staphylococci not susceptible to vancomycin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of telavancin in the treatment of experimental endocarditis due to glycopeptide-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Jul;51(7):2373-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01266-06. Epub 2007 May 7. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17485502 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence of less severe aortic valve destruction after treatment of experimental staphylococcal endocarditis with vancomycin and dexamethasone.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001 Dec;45(12):3531-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.45.12.3531-3537.2001. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001. PMID: 11709335 Free PMC article.
-
Activity of telavancin against heterogeneous vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus (hVISA) in vitro and in an in vivo mouse model of bacteraemia.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2010 Apr;65(4):725-8. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkq028. Epub 2010 Feb 5. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2010. PMID: 20139142
-
The role of vancomycin in the treatment paradigm.Clin Infect Dis. 2006 Jan 1;42 Suppl 1:S51-7. doi: 10.1086/491714. Clin Infect Dis. 2006. PMID: 16323121 Review.
-
New agents for Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis.Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2006 Dec;19(6):544-50. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0b013e328010683e. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2006. PMID: 17075329 Review.
Cited by
-
Native valve endocarditis caused by Corynebacterium striatum with heterogeneous high-level daptomycin resistance: collateral damage from daptomycin therapy?Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Jun;56(6):3461-4. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00046-12. Epub 2012 Mar 26. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22450978 Free PMC article.
-
The antifungal vaccine derived from the recombinant N terminus of Als3p protects mice against the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus.Infect Immun. 2008 Oct;76(10):4574-80. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00700-08. Epub 2008 Jul 21. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18644876 Free PMC article.
-
Telavancin Is Active against Experimental Aortic Valve Endocarditis Caused by Daptomycin- and Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Strains.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 Jan 24;61(2):e01877-16. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01877-16. Print 2017 Feb. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017. PMID: 27872064 Free PMC article.
-
Further insights into the mode of action of the lipoglycopeptide telavancin through global gene expression studies.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Jun;56(6):3157-64. doi: 10.1128/AAC.05403-11. Epub 2012 Mar 12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22411615 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacodynamics of telavancin studied in an in vitro pharmacokinetic model of infection.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011 Feb;55(2):867-73. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00933-10. Epub 2010 Nov 15. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21078943 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hegde, S. S., N. Reyes, T. Wiens, N. Vanasse, R. Skinner, J. McCullough, K. Kaniga, J. Pace, R. Thomas, J. P. Shaw, G. Obedencio, and J. K. Judice. 2004. Pharmacodynamics of telavancin (TD-6424), a novel bactericidal agent, against gram-positive bacteria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 48:3043-3050. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Higgins, D. L., R. Chang, D. Debabov, J. Leung, T. Wu, K. M. Krause, E. Sandvik, J. Hubbard, K. Kaniga, D. E. Schmidt Jr., Q. Gao, R. T. Cass, D. Karr, B. M. Benton, and P. P. Humphrey. 2005. Telavancin, a multifunctional lipoglycopeptide, disrupts both cell wall synthesis and cell membrane integrity in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 49:1127-1134. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Judice, J. K., and J. L. Pace. 2003. Semi-synthetic glycopeptide antibacterials. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 13:4165-4168. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous