Modulation of CaV2.1 channels by the neuronal calcium-binding protein visinin-like protein-2
- PMID: 16049183
- PMCID: PMC6724833
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0447-05.2005
Modulation of CaV2.1 channels by the neuronal calcium-binding protein visinin-like protein-2
Abstract
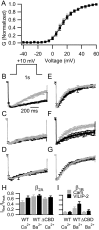
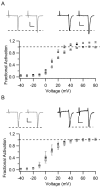
CaV2.1 channels conduct P/Q-type Ca2+ currents that are modulated by calmodulin (CaM) and the structurally related Ca2+-binding protein 1 (CaBP1). Visinin-like protein-2 (VILIP-2) is a CaM-related Ca2+-binding protein expressed in the neocortex and hippocampus. Coexpression of CaV2.1 and VILIP-2 in tsA-201 cells resulted in Ca2+ channel modulation distinct from CaM and CaBP1. CaV2.1 channels with beta2a subunits undergo Ca2+-dependent facilitation and inactivation attributable to association of endogenous Ca2+/CaM. VILIP-2 coexpression does not alter facilitation measured in paired-pulse experiments but slows the rate of inactivation to that seen without Ca2+/CaM binding and reduces inactivation of Ca2+ currents during trains of repetitive depolarizations. CaV2.1 channels with beta1b subunits have rapid voltage-dependent inactivation, and VILIP-2 has no effect on the rate of inactivation or facilitation of the Ca2+ current. In contrast, when Ba2+ replaces Ca2+ as the charge carrier, VILIP-2 slows inactivation. The effects of VILIP-2 are prevented by deletion of the CaM-binding domain (CBD) in the C terminus of CaV2.1 channels. However, both the CBD and an upstream IQ-like domain must be deleted to prevent VILIP-2 binding. Our results indicate that VILIP-2 binds to the CBD and IQ-like domains of CaV2.1 channels like CaM but slows inactivation, which enhances facilitation of CaV2.1 channels during extended trains of stimuli. Comparison of VILIP-2 effects with those of CaBP1 indicates striking differences in modulation of both facilitation and inactivation. Differential regulation of CaV2.1 channels by CaM, VILIP-2, CaBP1, and other neurospecific Ca2+-binding proteins is a potentially important determinant of Ca2+ entry in neurotransmission.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Molecular determinants of modulation of CaV2.1 channels by visinin-like protein 2.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jan 2;287(1):504-513. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.292581. Epub 2011 Nov 10. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22074920 Free PMC article.
-
Differential regulation of CaV2.1 channels by calcium-binding protein 1 and visinin-like protein-2 requires N-terminal myristoylation.J Neurosci. 2005 Jul 27;25(30):7071-80. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0452-05.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16049184 Free PMC article.
-
Fine-tuning synaptic plasticity by modulation of Ca(V)2.1 channels with Ca2+ sensor proteins.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Oct 16;109(42):17069-74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1215172109. Epub 2012 Oct 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23027954 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Visinin-Like Protein-1 in the Pathophysiology of Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;47(1):17-32. doi: 10.3233/JAD-150060. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015. PMID: 26402751 Review.
-
Presynaptic Calcium Channels.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 6;20(9):2217. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092217. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31064106 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptional profile changes caused by noise-induced tinnitus in the cochlear nucleus and inferior colliculus of the rat.Ann Med. 2024 Dec;56(1):2402949. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2402949. Epub 2024 Sep 13. Ann Med. 2024. PMID: 39268590 Free PMC article.
-
The C-terminus of Kv7 channels: a multifunctional module.J Physiol. 2008 Apr 1;586(7):1803-10. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.149187. Epub 2008 Jan 24. J Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18218681 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Short-term presynaptic plasticity.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012 Jul 1;4(7):a005702. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a005702. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012. PMID: 22751149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calcium sensor regulation of the CaV2.1 Ca2+ channel contributes to long-term potentiation and spatial learning.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Nov 15;113(46):13209-13214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1616206113. Epub 2016 Oct 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27799552 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular determinants of modulation of CaV2.1 channels by visinin-like protein 2.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jan 2;287(1):504-513. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.292581. Epub 2011 Nov 10. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22074920 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ames JB, Ishima R, Tanaka T, Gordon JI, Stryer L, Ikura M (1997) Molecular mechanics of calcium-myristoyl switches. Nature 389: 198-202. - PubMed
-
- Arikkath J, Campbell KP (2003) Auxiliary subunits: essential components of the voltage-gated calcium channel complex. Curr Opin Neurobiol 13: 298-307. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein HG, Baumann B, Danos P, Diekmann S, Bogerts B, Gundelfinger ED, Braunewell KH (1999) Regional and cellular distribution of neural visinin-like protein immunoreactivities (VILIP-1 and VILIP-3) in human brain. J Neurocytol 28: 655-662. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein HG, Becker A, Keilhoff G, Spilker C, Gorczyca WA, Braunewell KH, Grecksch G (2003) Brain region-specific changes in the expression of calcium sensor proteins after repeated applications of ketamine to rats. Neurosci Lett 339: 95-98. - PubMed
-
- Burgess DL, Biddlecome GH, McDonough SI, Diaz ME, Zilinski CA, Bean BP, Campbell KP, Noebels JL (1999) Beta subunit reshuffling modifies N- and P/Q-type Ca2+ channel subunit compositions in lethargic mouse brain. Mol Cell Neurosci 13: 293-311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
