MUC4 expression is a novel prognostic factor in patients with invasive ductal carcinoma of the pancreas
- PMID: 16049287
- PMCID: PMC1770880
- DOI: 10.1136/jcp.2004.023572
MUC4 expression is a novel prognostic factor in patients with invasive ductal carcinoma of the pancreas
Abstract
Background: Many patients with invasive ductal carcinoma of the pancreas (IDC) have a poor outcome. MUC4 expression has been implicated as a marker for diagnosis and progression of IDC, but there are no studies of the relation between MUC4 expression and patient prognosis in IDC.
Aims: To investigate the prognostic significance of MUC4 expression in IDC.
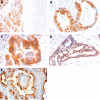
Methods: The expression profiles of MUC4, ErbB2, p27, and MUC1 were investigated in IDC tissues from 135 patients by means of immunohistochemistry.
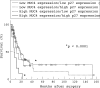
Results: MUC4 was expressed in 43 of the 135 patients with IDC (31.9%). The survival of 21 patients with high MUC4 expression (>20% of neoplastic cells stained) was significantly worse than that of the 114 patients with low MUC4 expression (<20% of neoplastic cells stained) (p = 0.0043). Univariate analysis showed that high MUC4 expression (p = 0.0061), large primary tumour status (>T2) (p = 0.0436), distant metastasis (p = 0.0383), lymphatic invasion (p = 0.0243), and surgical margins (p = 0.0333) were significant risk factors affecting the outcome of patients with IDC. Backward stepwise multivariate analysis showed that MUC4 expression (p = 0.0121), lymph node metastasis (p = 0.0245), and lymphatic invasion (p = 0.0239) were significant independent risk factors. ErbB2, p27, and MUC1 were not independent risk factors.
Conclusions: This study shows that MUC4 expression in IDC is a new independent factor for poor prognosis and predicts the outcome of patients with IDC.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MUC4 is a novel prognostic factor of extrahepatic bile duct carcinoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2006 Jul 15;12(14 Pt 1):4257-64. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-2814. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16857800
-
Aberrant methylation of MUC1 and MUC4 promoters are potential prognostic biomarkers for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 5;7(27):42553-42565. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9924. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27283771 Free PMC article.
-
MUC4 expression correlates with poor prognosis in small-sized lung adenocarcinoma.Lung Cancer. 2007 Feb;55(2):195-203. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2006.10.013. Epub 2006 Nov 28. Lung Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17126950
-
Significance of mucin expression in pancreatobiliary neoplasms.J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2010 Mar;17(2):108-24. doi: 10.1007/s00534-009-0174-7. Epub 2009 Sep 29. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2010. PMID: 19787286 Review.
-
MUC4 mucin- a therapeutic target for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2017 Jul;21(7):657-669. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2017.1323880. Epub 2017 May 29. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2017. PMID: 28460571 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting interleukin-17 receptor B enhances gemcitabine sensitivity through downregulation of mucins in pancreatic cancer.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 20;10(1):17817. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73659-z. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33082357 Free PMC article.
-
Radioimmunotherapy--a potential novel tool for pancreatic cancer therapy?Tumour Biol. 2015 Jun;36(6):4053-62. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3479-y. Epub 2015 Apr 30. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 25926382 Review.
-
Monoclonal antibodies recognizing the non-tandem repeat regions of the human mucin MUC4 in pancreatic cancer.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23344. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023344. Epub 2011 Aug 23. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21886786 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and therapeutic implications of a novel immunohistochemical panel detecting duodenal mucosal invasion by pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013 Oct 15;6(11):2476-86. eCollection 2013. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013. PMID: 24228110 Free PMC article.
-
Bile accelerates carcinogenic processes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells through the overexpression of MUC4.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 16;10(1):22088. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-79181-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33328627 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Matsuno S, Egawa S, Fukuyama S, et al. Pancreatic cancer registry in Japan: 20 years of experience. Pancreas 2004;28:219–30. - PubMed
-
- Isaji S, Kawarada Y, Uemoto S. Classification of pancreatic cancer: comparison of Japanese and UICC classifications. Pancreas 2004;28:231–4. - PubMed
-
- Egawa S, Takeda K, Fukuyama S, et al. Clinicopathological aspects of small pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 2004;28:235–40. - PubMed
-
- Yonezawa S, Sato E. Expression of mucin antigens in human cancers and its relationship with malignancy potential. Pathol Int 1997;47:813–30. - PubMed
-
- D’Cruz OJ, Dunn TS, Pichan P, et al. Antigenic cross-reactivity of human tracheal mucin with human sperm and trophoblasts correlates with the expression of mucin 8 gene messenger ribonucleic acid in reproductive tract tissues. Fertil Steril 1996;66:316–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
