Experience and strategy for the molecular testing of Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- PMID: 16049303
- PMCID: PMC1867542
- DOI: 10.1016/S1525-1578(10)60560-0
Experience and strategy for the molecular testing of Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Abstract
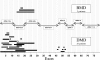
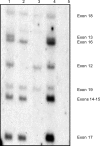
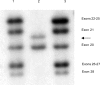
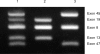
Mutations in the dystrophin gene result in both Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies (DMD and BMD). Approximately two-thirds of the affected patients have large deletions or duplications. Using the multiplex polymerase chain reaction and Southern blotting techniques, the detection of these larger mutations is relatively straightforward. Detection of the point mutations in the remaining one-third of the patients has been challenging, mainly due to the large gene size and lack of hotspots or prevalent mutations. However, with the addition of some of the newer molecular screening methods, it is becoming more feasible for clinical laboratories to test for point mutations in the larger genes like dystrophin. Here we review the clinical features, describe the mutation distributions, evaluate current molecular strategies, and illustrate how the genetic findings have impacted the current clinical diagnostics of Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies.
Figures


References
-
- Moser H. Duchenne muscular dystrophy: pathogenetic aspects and genetic prevention. Hum Genet. 1984;66:17–40. - PubMed
-
- Emery AEH. Muscle histology and creatine kinase levels in the fetus in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nature. 1977;266:472–473. - PubMed
-
- Emery AEH. New York: Oxford University Press; Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. (ed 2.) 1993
-
- Farah MG, Evans EB, Vignos PJ. Echocardiographic evaluation of left function in Duchenne’s muscular dystrophy. Am J Med. 1980;69:248–252. - PubMed
-
- Leibowitz D, Dubowitz V. Intellect and behavior in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Dev Med Neurol. 1981;23:577–590. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

