Loss of fibroblast Thy-1 expression correlates with lung fibrogenesis
- PMID: 16049324
- PMCID: PMC1603564
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)62982-3
Loss of fibroblast Thy-1 expression correlates with lung fibrogenesis
Abstract
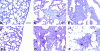
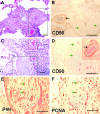
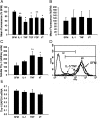
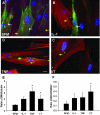
Fibroblasts consist of heterogeneous subpopulations that have distinct roles in fibrotic responses. Previously we reported enhanced proliferation in response to fibrogenic growth factors and selective activation of latent transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta in fibroblasts lacking cell surface expression of Thy-1 glycoprotein, suggesting that Thy-1 modulates the fibrogenic potential of fibroblasts. Here we report that compared to controls Thy-1-/- C57BL/6 mice displayed more severe histopathological lung fibrosis, greater accumulation of lung collagen, and increased TGF-beta activation in the lungs 14 days after intratracheal bleomycin. The majority of cells demonstrating TGF-beta activation and myofibroblast differentiation in bleomycin-induced lesions were Thy-1-negative. Histological sections from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis demonstrated absent Thy-1 staining within fibroblastic foci. Normal lung fibroblasts, in both mice and humans, were predominantly Thy-1-positive. The fibrogenic cytokines interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha induced loss of fibroblast Thy-1 surface expression in vitro, which was associated with Thy-1 shedding, Smad phosphorylation, and myofibroblast differentiation. These results suggest that fibrogenic injury promotes loss of lung fibroblast Thy-1 expression, resulting in enhanced fibrogenesis.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Thy-1 expression regulates the ability of rat lung fibroblasts to activate transforming growth factor-beta in response to fibrogenic stimuli.Am J Pathol. 2004 Aug;165(2):659-69. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)63330-5. Am J Pathol. 2004. PMID: 15277239 Free PMC article.
-
Latent transforming growth factor-beta-binding protein-4 regulates transforming growth factor-beta1 bioavailability for activation by fibrogenic lung fibroblasts in response to bleomycin.Am J Pathol. 2009 Jan;174(1):21-33. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.080620. Epub 2008 Dec 4. Am J Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19056849 Free PMC article.
-
Lung fibroblast alpha-smooth muscle actin expression and contractile phenotype in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis.Am J Pathol. 1996 Feb;148(2):527-37. Am J Pathol. 1996. PMID: 8579115 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingolipids in pulmonary fibrosis.Adv Biol Regul. 2015 Jan;57:55-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2014.09.008. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Adv Biol Regul. 2015. PMID: 25446881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thy-1, a versatile modulator of signaling affecting cellular adhesion, proliferation, survival, and cytokine/growth factor responses.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Oct;1763(10):991-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.08.008. Epub 2006 Aug 18. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 16996153 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic regulation of Thy-1 gene expression by histone modification is involved in lipopolysaccharide-induced lung fibroblast proliferation.J Cell Mol Med. 2013 Jan;17(1):160-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2012.01659.x. Epub 2013 Jan 11. J Cell Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23305530 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and cellular mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis.Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 2012 Jul 23;5(1):11. doi: 10.1186/1755-1536-5-11. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 2012. PMID: 22824096 Free PMC article.
-
Thy-1 attenuates TNF-alpha-activated gene expression in mouse embryonic fibroblasts via Src family kinase.PLoS One. 2010 Jul 19;5(7):e11662. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011662. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20657842 Free PMC article.
-
The Genetic and Epigenetic Footprint in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Familial Pulmonary Fibrosis: A State-of-the-Art Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Dec 9;12(12):3107. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12123107. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36553114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The quest of cell surface markers for stem cell therapy.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Jan;78(2):469-495. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03602-y. Epub 2020 Jul 24. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 32710154 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Crystal RG, Bitterman PB, Mossman B, Schwarz MI, Sheppard D, Almasy L, Chapman HA, Friedman SL, King TE, Jr, Leinwand LA, Liotta L, Martin GR, Schwartz DA, Schultz GS, Wagner CR, Musson RA. Future research directions in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: summary of a National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute working group. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;166:236–246. - PubMed
-
- King TE, Schwarz MI, Brown K, Tooze JA, Colby TV, Waldron JA, Flint A, Thurlbeck W, Cherniack RM. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Relationship between histopathologic features and mortality. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;164:1025–1032. - PubMed
-
- Nicholson AG, Fulford LG, Colby TV, du Bois RM, Hansell DM, Wells AU. The relationship between individual histologic features and disease progression in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;166:173–177. - PubMed
-
- Katzenstein AL, Myers JL. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: clinical relevance of pathologic classification. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;157:1301–1315. - PubMed
-
- Selman M, King TE, Pardo A. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: prevailing and evolving hypotheses about its pathogenesis and implications for therapy. Ann Intern Med. 2001;134:136–151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

