Changes in interstitial cells of Cajal at the deep muscular plexus are associated with loss of distention-induced burst-type muscle activity in mice infected by Trichinella spiralis
- PMID: 16049330
- PMCID: PMC1603561
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)62988-4
Changes in interstitial cells of Cajal at the deep muscular plexus are associated with loss of distention-induced burst-type muscle activity in mice infected by Trichinella spiralis
Abstract
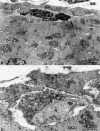
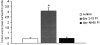
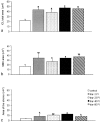
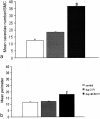
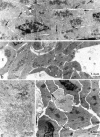
The physiology and pathophysiology of the network of interstitial cells of Cajal associated with the deep muscular plexus (ICC-DMP) of the small intestine are still poorly understood. The objectives of the present study were to evaluate the effects of inflammation associated with Trichinella spiralis infection on the ICC-DMP and to correlate loss of function with structural changes in these cells and associated structures. We used immunohistochemistry, electron microscopy, and assessment of distention-inducing electrophysiological parameters in vitro. Damage to ICC-DMP was associated with a loss of distention-induced patterns of electrical activity normally associated with distention-induced peristalsis. Consistently, the timing of recovery of ICC-DMP paralleled the timing of recovery of the distention-induced activity. Nerve varicosities associated with ICC-DMP including cholinergic nerves, assessed by immunoelectron microscopy and whole mount double labeling, paralleled injury to ICC-DMP thus contributing to impaired excitatory innervation of smooth muscle cells. Major additional changes included a remodeling of the inner circular muscle layer, which may affect long-term sensitivity to distention after infection. In conclusion, transient injury to ICC-DMP in response to T. spiralis infection is severe and associated with a complete lack of distention-induced burst-type muscle activity.
Figures


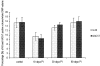





Similar articles
-
Interstitial cells of cajal and inflammation-induced motor dysfunction in the mouse small intestine.Gastroenterology. 2000 Dec;119(6):1590-9. doi: 10.1053/gast.2000.20221. Gastroenterology. 2000. PMID: 11113080
-
Pathology of interstitial cells of Cajal in relation to inflammation revealed by ultrastructure but not immunohistochemistry.Am J Pathol. 2002 Apr;160(4):1529-40. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)62579-5. Am J Pathol. 2002. PMID: 11943737 Free PMC article.
-
PKC-epsilon translocation in enteric neurons and interstitial cells of Cajal in response to muscarinic stimulation.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2003 Sep;285(3):G593-601. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00421.2002. Epub 2003 Apr 23. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12711590
-
Gap junctions in intestinal smooth muscle and interstitial cells of Cajal.Microsc Res Tech. 1999 Dec 1;47(5):309-20. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0029(19991201)47:5<309::AID-JEMT2>3.0.CO;2-K. Microsc Res Tech. 1999. PMID: 10602290 Review.
-
Identification of interstitial cells of Cajal. Significance for studies of human small intestine and colon.Dan Med Bull. 1994 Jun;41(3):275-93. Dan Med Bull. 1994. PMID: 7924459 Review.
Cited by
-
Ca2+-activated K+ current in freshly isolated c-Kit positive cells in guinea-pig stomach.J Korean Med Sci. 2009 Jun;24(3):384-91. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.3.384. Epub 2009 Jun 12. J Korean Med Sci. 2009. PMID: 19543421 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroinflammation in inflammatory bowel disease.J Neuroinflammation. 2010 Jul 8;7:37. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-7-37. J Neuroinflammation. 2010. PMID: 20615234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunoinflammation and functional gastrointestinal disorders.Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2012 Jul-Aug;18(4):225-9. doi: 10.4103/1319-3767.98420. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22824763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Substance P and Neurokinin 1 receptor - expression is affected in the ileum of mice with mutation in the W locus.J Cell Mol Med. 2006 Apr-Jun;10(2):511-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2006.tb00416.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2006. PMID: 16796816 Free PMC article.
-
Delayed development of interstitial cells of Cajal in the ileum of a human case of gastroschisis.J Cell Mol Med. 2008 Apr;12(2):471-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00277.x. Epub 2008 Feb 8. J Cell Mol Med. 2008. PMID: 18266958 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thuneberg L. Interstitial cells of Cajal: intestinal pacemaker cells? Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 1982;71:1–130. - PubMed
-
- Rumessen JJ, Thuneberg L, Mikkelsen HB. Plexus muscularis profundus and associated interstitial cells. II. Ultrastructural studies of mouse small intestine. Anat Rec. 1982;203:129–146. - PubMed
-
- Rumessen JJ, Thuneberg L. Plexus muscularis profundus and associated interstitial cells. I. Light microscopical studies of mouse small intestine. Anat Rec. 1982;203:115–127. - PubMed
-
- Faussone Pellegrini MS, Cortesini C. Some ultrastructural features of the muscular coat of human small intestine. Acta Anat (Basel) 1983;115:47–68. - PubMed
-
- Kobilo T, Szurszewski JH, Farrugia G, Hanani M. Coupling and innervation patterns of interstitial cells of Cajal in the deep muscular plexus of the guinea-pig. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2003;15:635–641. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

