Heat-shock cognate 70 is required for the activation of heat-shock factor 1 in mammalian cells
- PMID: 16050811
- PMCID: PMC1317673
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20050412
Heat-shock cognate 70 is required for the activation of heat-shock factor 1 in mammalian cells
Abstract
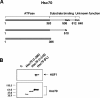
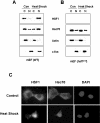
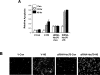
HSF1 (heat-shock factor 1) plays an essential role in mediating the appropriate cellular response to diverse forms of physiological stresses. However, it is not clear how HSF1 is regulated by interacting proteins under normal and stressful conditions. In the present study, Hsc70 (heat-shock cognate 70) was identified as a HSF1-interacting protein using the TAP (tandem affinity purification) system and MS. HSF1 can interact with Hsc70 in vivo and directly in vitro. Interestingly, Hsc70 is required for the regulation of HSF1 during heat stress and subsequent target gene expression in mammalian cells. Moreover, cells transfected with siRNAs (small interfering RNAs) targeted to Hsc70 showed greatly decreased HSF1 activation with expression of HSF1 target genes being dramatically reduced. Finally, loss of Hsc70 expression in cells resulted in an increase in stress-induced apoptosis. These results indicate that Hsc70 is a necessary and critical regulator of HSF1 activities.
Figures



References
-
- Parsell D. A., Lindquist S. The function of heat-shock proteins in stress tolerance: degradation and reactivation of damaged proteins. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1993;27:437–496. - PubMed
-
- Morimoto R. I., Tissieres A., Georgopoulos C. Cold Spring Harbor Monograph Series, vol. 26. Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1994. The biology of the heat shock proteins and molecular chaperones; p. 610.
-
- Fink A. L. Chaperone-mediated protein folding. Physiol. Rev. 1999;79:425–449. - PubMed
-
- Kaufman R. J. Molecular chaperones and the heat shock response. Sponsored by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, 6–10 May 1998. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1999;1423:R13–R27. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

