Resistance to store depletion-induced endothelial injury in rat lung after chronic heart failure
- PMID: 16051904
- PMCID: PMC2718399
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.200506-847OC
Resistance to store depletion-induced endothelial injury in rat lung after chronic heart failure
Abstract
Rationale: In chronic heart failure, the lung endothelial permeability response to angiotensin II or thapsigargin-induced store depletion is ablated, although the mechanisms are not understood.
Objectives: To determine whether the ablated permeability response to store depletion during heart failure was due to impaired expression of store operated Ca2+ channels in lung endothelium.
Methods: Heart failure was induced by aortocaval fistula in rats. Permeability was measured in isolated lungs using the filtration coefficient and a low Ca2+/Ca2+ add-back strategy to identify the component of the permeability response dependent on Ca2+ entry.
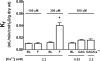
Main results: In fistulas, right ventricular mass and left ventricular end diastolic pressure were increased and left ventricular shortening fraction decreased compared with shams. Thapsigargin-induced store depletion increased lung endothelial permeability in shams, but not in fistulas. Permeability increased in both groups after the Ca2+ ionophore A23187 or 14,15-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid, independent of store depletion. A diacylglycerol analog had no impact on permeability. Increased distance between the endoplasmic reticulum and the plasmalemmal membrane was ruled out as a mechanism for the loss of the permeability response to store depletion. Endothelial expression of the endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase was not altered in fistulas compared with shams, whereas the store-operated canonical transient receptor potential channels 1, 3, and 4 were downregulated in extraalveolar vessel endothelium.
Conclusions: We conclude that the adaptive mechanism limiting store depletion-induced endothelial lung injury in the aortocaval model of heart failure involves downregulation of store-operated Ca2+ channels.
Figures






References
-
- Rame JE, Dries DL, Drazner MH. The prognostic value of the physical examination in patients with chronic heart failure. Congest Heart Fail 2003;9:170–178. - PubMed
-
- Riegger GA, Liebau G, Bauer E, Kochsiek K. Vasopressin and renin in high output heart failure of rats: hemodynamic effects of elevated plasma hormone levels. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1985;7:1–5. - PubMed
-
- Stevenson LW, Perloff JK. The limited reliability of physical signs for estimating hemodynamics in chronic heart failure. JAMA 1989;261:884–888. - PubMed
-
- Huang W, Kingsbury MP, Turner MA, Donnelly JL, Flores NA, Sheridan DJ. Capillary filtration is reduced in lungs adapted to chronic heart failure: morphological and haemodynamic correlates. Cardiovasc Res 2001;49:207–217. - PubMed
-
- Kay JM, Edwards FR. Ultrastructure of the alveolar-capillary wall in mitral stenosis. J Pathol 1973;111:239–245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

