Membrane-associated zinc peptidase families: comparing ACE and ACE2
- PMID: 16054014
- PMCID: PMC7105243
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2004.10.010
Membrane-associated zinc peptidase families: comparing ACE and ACE2
Abstract
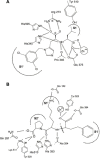
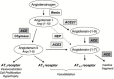
In contrast to the relatively ubiquitous angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), expression of the mammalian ACE homologue, ACE2, was initially described in the heart, kidney and testis. ACE2 is a type I integral membrane protein with its active site domain exposed to the extracellular surface of endothelial cells and the renal tubular epithelium. Here ACE2 is poised to metabolise circulating peptides which may include angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor and the product of angiotensin I cleavage by ACE. To this end, ACE2 may counterbalance the effects of ACE within the renin-angiotensin system (RAS). Indeed, ACE2 has been implicated in the regulation of heart and renal function where it is proposed to control the levels of angiotensin II relative to its hypotensive metabolite, angiotensin-(1-7). The recent solution of the structure of ACE2, and ACE, has provided new insight into the substrate and inhibitor profiles of these two key regulators of the RAS. As the complexity of this crucial pathway is unravelled, there is a growing interest in the therapeutic potential of agents that modulate the activity of ACE2.
Figures
References
-
- Turner A.J., Hooper N.M. The angiotensin-converting enzyme gene family: genomics and pharmacology. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2002;23:177. - PubMed
-
- Campbell D.J. Tissue renin–angiotensin system: sites of angiotensin formation. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1987;10:S1–S8. - PubMed
-
- Yang H.Y.T., Erdos E.G., Levin Y. A dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase that converts angiotensin I and inactivates bradykinin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1970;214:374–376. - PubMed
-
- Tipnis S.R., Hooper N.M., Hyde R., Karran E., Christie G., Turner A.J. A human homologue of angiotensin-converting enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:33238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

