Cardiac and skeletal muscle disorders caused by mutations in the intracellular Ca2+ release channels
- PMID: 16075044
- PMCID: PMC1180555
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI25664
Cardiac and skeletal muscle disorders caused by mutations in the intracellular Ca2+ release channels
Abstract
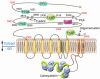
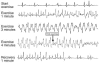
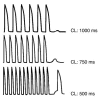
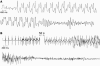
Here we review the current knowledge about the mutations of the gene encoding the cardiac ryanodine receptor (RyR2) that cause cardiac arrhythmias. Similarities between the mutations identified in the RyR2 gene and those found in the gene RyR1 that cause malignant hyperthermia and central core disease are discussed. In vitro functional characterization of RyR1 and RyR2 mutants is reviewed, with a focus on the contribution that in vitro expression studies have made to our understanding of related human diseases.
Figures

References
-
- Gillard EF, et al. Polymorphisms and deduced amino acid substitutions in the coding sequence of the ryanodine receptor (RYR1) gene in individuals with malignant hyperthermia. Genomics. 1992;13:1247–1254. - PubMed
-
- Priori SG, et al. Mutations in the cardiac ryanodine receptor gene (hRyR2) underlie catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia. Circulation. 2001;103:196–200. - PubMed
-
- Otsu K, et al. Chromosome mapping of five human cardiac and skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum protein genes. Genomics. 1993;17:507–509. - PubMed
-
- Tiso N, et al. Identification of mutations in the cardiac ryanodine receptor gene in families affected with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy type 2 (ARVD2) Hum. Mol. Genet. 2001;10:189–194. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

