ROS generated by pollen NADPH oxidase provide a signal that augments antigen-induced allergic airway inflammation
- PMID: 16075057
- PMCID: PMC1180538
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI24422
ROS generated by pollen NADPH oxidase provide a signal that augments antigen-induced allergic airway inflammation
Abstract
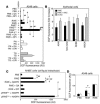
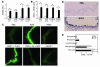
Pollen exposure induces allergic airway inflammation in sensitized subjects. The role of antigenic pollen proteins in the induction of allergic airway inflammation is well characterized, but the contribution of other constituents in pollen grains to this process is unknown. Here we show that pollen grains and their extracts contain intrinsic NADPH oxidases. The pollen NADPH oxidases rapidly increased the levels of ROS in lung epithelium as well as the amount of oxidized glutathione (GSSG) and 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) in airway-lining fluid. These oxidases, as well as products of oxidative stress (such as GSSG and 4-HNE) generated by these enzymes, induced neutrophil recruitment to the airways independent of the adaptive immune response. Removal of pollen NADPH oxidase activity from the challenge material reduced antigen-induced allergic airway inflammation, the number of mucin-containing cells in airway epithelium, and antigen-specific IgE levels in sensitized mice. Furthermore, challenge with Amb a 1, the major antigen in ragweed pollen extract that does not possess NADPH oxidase activity, induced low-grade allergic airway inflammation. Addition of GSSG or 4-HNE to Amb a 1 challenge material boosted allergic airway inflammation. We propose that oxidative stress generated by pollen NADPH oxidases (signal 1) augments allergic airway inflammation induced by pollen antigen (signal 2).
Figures






Comment in
-
Spring brings breezes, wheezes, and pollen oxidases.J Clin Invest. 2005 Aug;115(8):2067-9. doi: 10.1172/JCI26023. J Clin Invest. 2005. PMID: 16075049 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bousquet J, et al. Eosinophilic inflammation in asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990;323:1033–1039. - PubMed
-
- Sur S, et al. Sudden-onset fatal asthma. A distinct entity with few eosinophils and relatively more neutrophils in the airway submucosa? Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1993;148:713–719. - PubMed
-
- Gleich GJ, et al. The eosinophilic leukocyte and the pathology of fatal bronchial asthma: evidence for pathologic heterogeneity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1987;80:412–415. - PubMed
-
- Lee JJ, et al. Defining a link with asthma in mice congenitally deficient in eosinophils. Science. 2004;305:1773–1776. - PubMed
-
- Sur S, Kita H, Gleich GJ, Chenier TC, Hunt LW. Eosinophil recruitment is associated with IL-5, but not with RANTES, twenty-four hours after allergen challenge. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1996;97:1272–1278. - PubMed

