Clinical significance of the quantitative assessment of the cytosolic concentration of HER-2/neu protein in breast cancer by immunoenzymatic assay (ELISA)
- PMID: 16075281
- PMCID: PMC12161204
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-005-0022-3
Clinical significance of the quantitative assessment of the cytosolic concentration of HER-2/neu protein in breast cancer by immunoenzymatic assay (ELISA)
Abstract
Purpose: Retrospective analysis to assess the prognostic and predictive value of HER-2/ neu expression in breast tumors, quantified by enzyme immunoassay (ELISA).
Methods: Quantification of HER-2/neu was performed on cytosolic extracts from 914 cases of primary invasive breast carcinomas. Relapse-free and overall survival data were available from 889 patients. The prognostic value of HER-2/neu levels was assessed considering them as a continuous, dichotomic or quartile variable.
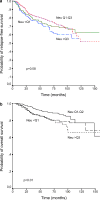
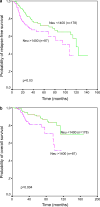
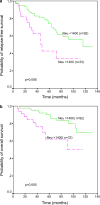
Results: Cytosolic HER-2/neu levels ranged widely in breast carcinomas (median: 746.5 NHU/mg; range: 2.8-80,000 NHU/mg protein). HER-2/neu protein levels were significantly higher in either moderately or poorly differentiated tumors, as well as in those showing a ductal histological type, aneuploidy or a high S-phase fraction. There was a significant and positive association between cytosolic and membranous HER-2/neu levels (n=162, r sub S=0.53; P<0.0001). In addition, cytosolic HER-2/neu level correlated weakly with progesterone receptors but not with estrogen receptors. Elevated cytosolic HER-2/neu levels (> or =1,400 NHU/mg protein) were associated with a high probability of both shortened relapse-free survival and overall survival. This same cut-off value was obtained when we divided the overall group of patients in a training set. However, this HER-2/neu value did not achieve any statistical significance in a validation set used to make sure that the cut-off was correct. Nevertheless, when we divided the obtained data into three different groups with respect to the quartile values (Q) of the intratumoral oncoprotein levels (< or = Q1 vs Q1-Q2 vs > Q3), we observed that patients with either low HER-2/ neu levels (< or = Q1) or high HER-2/neu levels (> Q3) had shorter both relapse-free survival and overall survival curves than those patients with intermediate HER-2/neu levels. On the other hand, high HER-2/neu levels predicted a poor response to adjuvant chemotherapy but not to adjuvant hormonal therapy with tamoxifen.
Conclusions: The results of the present investigation indicate that by quantitatively determining the content of HER-2/neu oncoprotein, groups of high-risk breast cancer patients could be identified, for a more effective clinical management.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Hormonal therapies for early breast cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2007 Jul;11(26):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-134. doi: 10.3310/hta11260. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 17610808
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allred DC, Clark GM, Tandon AK, Molina R, Tormey DC, Osborne CK, Gilchrist KW, Mansour EG, Abeloff M, Eudey L (1992) HER-2/neu in node-negative breast cancer: prognostic significance of overexpression influenced by the presence of in situ carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 10:599–605 - PubMed
-
- Andrulis IL, Bull SB, Blackstein ME, Sutherland D, Mak C, Sidlofsky S, Pritzker KP, Hartwick RW, Hanna W, Lickley L, Wilkinson R, Qizilbash A, Ambus U, Lipa M, Weizel H, Katz A, Baida M, Mariz S, Stoik G, Dacamara P, Strongitharm D, Geddie W, McCready D (1998) neu/erbB-2 amplification identifies a poor-prognosis group of women with node-negative breast cancer. Toronto Breast Cancer Study Group. J Clin Oncol 16:1340–1349 - PubMed
-
- Benz C, Tripathy D (2000) ErbB-2 overexpression in breast cancer: biology and clinical translation. J Women’s Cancer 2:33–40
-
- Berger MS, Locher GW, Saurer S, Gullick WJ, Waterfield MD, Groner B, Hynes NE (1988) Correlation of c-erbB-2 gene amplification and protein expression in human breast carcinoma with nodal status and nuclear grading. Cancer Res 48:1238–1243 - PubMed
-
- Berry DA, Muss HB, Thor AD, Dressler L, Liu ET, Broadwater G, Budman DR, Henderson IC, Barcos M, Hayes D, Norton L (2000) HER-2/neu and p53 expression versus tamoxifen resistance in estrogen receptor-positive, node-positive breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 18:3471–3479 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

