Durable hematologic complete response and suppression of HTLV-1 viral load following alemtuzumab in zidovudine/IFN-{alpha}-refractory adult T-cell leukemia
- PMID: 16076875
- PMCID: PMC1895052
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2005-01-0335
Durable hematologic complete response and suppression of HTLV-1 viral load following alemtuzumab in zidovudine/IFN-{alpha}-refractory adult T-cell leukemia
Abstract
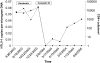
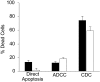
Adult T-cell leukemia (ATL) is a highly chemoresistant and usually fatal T-cell malignancy due to the human T-cell lymphotropic virus-1 (HTLV-1). After chemotherapy failure, antiretrovirals and interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha) produce brief responses followed by progression and death. More effective agents and new approaches to detect and treat minimal residual disease are needed. ATL cells express CD52, the target of the antibody alemtuzumab, which is active in a preclinical model of ATL and is cytotoxic for p53-deficient cells. A patient with refractory chronic ATL in transformation achieved longer than a 1-year complete hematologic response following 12 weeks of outpatient subcutaneous alemtuzumab. Persistent suppression of HTLV-1 viral load, even at recovery of T cells, after alemtuzumab and efficient in vitro complement-mediated cytotoxicity of primary ATL cells with mutated TP53 were observed. The unprecedented response and the profound suppression of HTLV-1 viral load observed in this patient suggest that further clinical investigation of alemtuzumab in ATL is warranted.
Figures
References
-
- Maloney EM, Blattner WA. HTLV-1 worldwide patterns and disease associations. In: Sugamura K, Uchiyama T, Matsuoka M, and Kannagi M, eds. Gann Monographs on Cancer Research. Vol 50. Japan Science Societies Press; 2003: 339-361.
-
- Yamada Y, Tomonaga M. The current status of therapy for adult T-cell leukaemia-lymphoma in Japan. Leuk Lymphoma. 2003;44: 611-618. - PubMed
-
- Hatta Y, Koeffler HP. Role of tumor suppressor genes in the development of adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL). Leukemia. 2002;16: 1069-1085. - PubMed
-
- Sun SC, Ballard DW. Persistent activation of NF-kappaB by the tax transforming protein of HTLV-1: hijacking cellular IkappaB kinases. Oncogene. 1999;18: 6948-6958. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

