Control of replication initiation and heterochromatin formation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by a regulator of meiotic gene expression
- PMID: 16077008
- PMCID: PMC1182343
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.334805
Control of replication initiation and heterochromatin formation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by a regulator of meiotic gene expression
Abstract
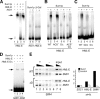
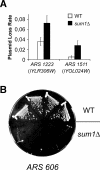
Heterochromatinization at the silent mating-type loci HMR and HML in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is achieved by targeting the Sir complex to these regions via a set of anchor proteins that bind to the silencers. Here, we have identified a novel heterochromatin-targeting factor for HML, the protein Sum1, a repressor of meiotic genes during vegetative growth. Sum1 bound both in vitro and in vivo to HML via a functional element within the HML-E silencer, and sum1Delta caused HML derepression. Significantly, Sum1 was also required for origin activity of HML-E, demonstrating a role of Sum1 in replication initiation. In a genome-wide search for Sum1-regulated origins, we identified a set of autonomous replicative sequences (ARS elements) that bound both the origin recognition complex and Sum1. Full initiation activity of these origins required Sum1, and their origin activity was decreased upon removal of the Sum1-binding site. Thus, Sum1 constitutes a novel global regulator of replication initiation in yeast.
Figures




References
-
- Beall E.L., Manak, J.R., Zhou, S., Bell, M., Lipsick, J.S., and Botchan, M.R. 2002. Role for a Drosophila Myb-containing protein complex in site-specific DNA replication. Nature 420: 833-837. - PubMed
-
- Bell S.P. and Dutta, A. 2002. DNA replication in eukaryotic cells. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 71: 333-374. - PubMed
-
- Bell S.P., Kobayashi, R., and Stillman, B. 1993. Yeast origin recognition complex functions in transcription silencing and DNA replication. Science 262: 1844-1849. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
