Upstream migration of Xylella fastidiosa via pilus-driven twitching motility
- PMID: 16077100
- PMCID: PMC1196070
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.187.16.5560-5567.2005
Upstream migration of Xylella fastidiosa via pilus-driven twitching motility
Abstract
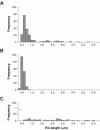
Xylella fastidiosa is a xylem-limited nonflagellated bacterium that causes economically important diseases of plants by developing biofilms that block xylem sap flow. How the bacterium is translocated downward in the host plant's vascular system against the direction of the transpiration stream has long been a puzzling phenomenon. Using microfabricated chambers designed to mimic some of the features of xylem vessels, we discovered that X. fastidiosa migrates via type IV-pilus-mediated twitching motility at speeds up to 5 mum min(-1) against a rapidly flowing medium (20,000 mum min(-1)). Electron microscopy revealed that there are two length classes of pili, long type IV pili (1.0 to 5.8 mum) and short type I pili (0.4 to 1.0 mum). We further demonstrated that two knockout mutants (pilB and pilQ mutants) that are deficient in type IV pili do not twitch and are inhibited from colonizing upstream vascular regions in planta. In addition, mutants with insertions in pilB or pilQ (possessing type I pili only) express enhanced biofilm formation, whereas a mutant with an insertion in fimA (possessing only type IV pili) is biofilm deficient.
Figures






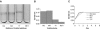

References
-
- Alm, R. A., and J. S. Mattick. 1997. Genes involved in the biogenesis and function of type-4 fimbriae in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Gene 192:89-98. - PubMed
-
- Bradley, D. E. 1980. A function of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO polar pili: twitching motility. Can. J. Microbiol. 26:146-154. - PubMed
-
- Chaudhury, M. K., and G. M. Whitesides. 1991. Direct measurement of interfacial interactions between semispherical lenses and flat sheets of poly(dimethylsiloxane) and their chemical derivatives. Langmuir 7:1013-1025.
-
- Davis, M. J., W. J. French, and N. W. Schaad. 1981. Axenic culture of the bacteria associated with phony disease of peach and plum leaf scald. Curr. Microbiol. 6:309-314.
-
- Feil, H., W. S. Feil, J. C. Detter, A. H. Purcell, and S. E. Lindow. 2003. Site-directed disruption of the fimA and fimF genes of Xylella fastidiosa. Phytopathology 93:675-682. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

