Interactions between partner switcher orthologs BtrW and BtrV regulate type III secretion in Bordetella
- PMID: 16077112
- PMCID: PMC1196064
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.187.16.5665-5676.2005
Interactions between partner switcher orthologs BtrW and BtrV regulate type III secretion in Bordetella
Abstract
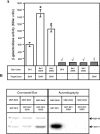
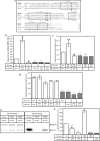
We have recently described a multicomponent cascade that regulates type III secretion in Bordetella. This cascade includes a group of proteins, BtrU, BtrW, and BtrV, that contain an array of domains that define partner-switching complexes previously characterized in gram-positive bacteria. BtrU contains a PP2C-like serine phosphatase domain, BtrW contains a serine kinase/anti-sigma factor motif, and BtrV includes an anti-sigma factor antagonist domain. On the basis of genetic studies and sequence similarity with the RsbU-RsbW-RsbV and SpoIIE-SpoIIAB-SpoIIAA partner switchers of Bacillus subtilis, a series of interactions between Bordetella orthologs have been proposed. Bacterial two-hybrid analysis, tagged protein pull-downs, and in vitro phosphorylation assays were used to characterize interactions between BtrW and BtrV. In addition, BtrV mutants predicted to mimic a constitutively phosphorylated form of BtrV or to be nonphosphorylatable and BtrW mutants defective in serine kinase activity or the ability to bind BtrV were constructed and analyzed. Our results demonstrate that (i) BtrW and BtrV interact with each other, (ii) BtrW phosphorylates BtrV at serine S55, (iii) the conserved serine residue S55 of BtrV plays a key role in BtrV-BtrW interactions, and (iv) the ability of BtrW to phosphorylate BtrV and disrupt BtrV-BtrW binding is essential for the type III secretion process.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Regulation of type III secretion in Bordetella.Mol Microbiol. 2004 May;52(4):1201-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04053.x. Mol Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15130135
-
Role of adenosine nucleotides in the regulation of a stress-response transcription factor in Bacillus subtilis.J Mol Biol. 1996 Jul 12;260(2):165-77. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0390. J Mol Biol. 1996. PMID: 8764398
-
SpoIIE governs the phosphorylation state of a protein regulating transcription factor sigma F during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Apr 16;93(8):3238-42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.8.3238. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996. PMID: 8622920 Free PMC article.
-
Control of the cell-specificity of sigma F activity in Bacillus subtilis.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1996 Apr 29;351(1339):537-42. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1996.0052. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1996. PMID: 8735276 Review.
-
Differential gene expression in genetically identical sister cells: the initiation of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.Mol Microbiol. 2005 May;56(3):578-89. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04594.x. Mol Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15819616 Review.
Cited by
-
The blue-light receptor YtvA acts in the environmental stress signaling pathway of Bacillus subtilis.J Bacteriol. 2006 Sep;188(17):6387-95. doi: 10.1128/JB.00691-06. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16923906 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of Chlamydia trachomatis with a small molecule inhibitor of the Yersinia type III secretion system disrupts progression of the chlamydial developmental cycle.Mol Microbiol. 2006 Sep;61(6):1543-55. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05347.x. Mol Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16968227 Free PMC article.
-
Distinctive topologies of partner-switching signaling networks correlate with their physiological roles.J Mol Biol. 2007 Jun 22;369(5):1333-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.04.021. Epub 2007 Apr 14. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17498739 Free PMC article.
-
Histidine-containing phosphotransfer protein-B (HptB) regulates swarming motility through partner-switching system in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 strain.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jan 13;287(3):1903-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.256586. Epub 2011 Nov 29. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22128156 Free PMC article.
-
Pertussis: Microbiology, Disease, Treatment, and Prevention.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2016 Jul;29(3):449-86. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00083-15. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27029594 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alper, S., L. Duncan, and R. Losick. 1994. An adenosine nucleotide switch controlling the activity of a cell type-specific transcription factor in B. subtilis. Cell 77:195-205. - PubMed
-
- Aravind, L., and E. V. Koonin. 2000. The STAS domain—a link between anion transporters and anti-sigma-factor antagonists. Curr. Biol. 10:R53-R55. - PubMed
-
- Beaucher, J., S. Rodrigue, P. E. Jacques, I. Smith, R. Brzezinski, and L. Gaudreau. 2002. Novel Mycobacterium tuberculosis anti-sigma factor antagonists control σF activity by distinct mechanisms. Mol. Microbiol. 45:1527-1540. - PubMed
-
- Campbell, E. A., S. Masuda, J. L. Sun, O. Muzzin, C. A. Olson, S. Wang, and S. A. Darst. 2002. Crystal structure of the Bacillus stearothermophilus anti-sigma factor SpoIIAB with the sporulation sigma factor σF. Cell 108:795-807. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

