Expanded metabolic reconstruction of Helicobacter pylori (iIT341 GSM/GPR): an in silico genome-scale characterization of single- and double-deletion mutants
- PMID: 16077130
- PMCID: PMC1196094
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.187.16.5818-5830.2005
Expanded metabolic reconstruction of Helicobacter pylori (iIT341 GSM/GPR): an in silico genome-scale characterization of single- and double-deletion mutants
Abstract
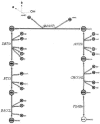
Helicobacter pylori is a human gastric pathogen infecting almost half of the world population. Herein, we present an updated version of the metabolic reconstruction of H. pylori strain 26695 based on the revised genome annotation and new experimental data. This reconstruction, iIT341 GSM/GPR, represents a detailed review of the current literature about H. pylori as it integrates biochemical and genomic data in a comprehensive framework. In total, it accounts for 341 metabolic genes, 476 intracellular reactions, 78 exchange reactions, and 485 metabolites. Novel features of iIT341 GSM/GPR include (i) gene-protein-reaction associations, (ii) elementally and charge-balanced reactions, (iii) more accurate descriptions of isoprenoid and lipopolysaccharide metabolism, and (iv) quantitative assessments of the supporting data for each reaction. This metabolic reconstruction was used to carry out in silico deletion studies to identify essential and conditionally essential genes in H. pylori. A total of 128 essential and 75 conditionally essential metabolic genes were identified. Predicted growth phenotypes of single knockouts were validated using published experimental data. In addition, in silico double-deletion studies identified a total of 47 synthetic lethal mutants involving 67 different metabolic genes in rich medium.
Figures


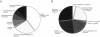

Similar articles
-
Genome-scale metabolic model of Helicobacter pylori 26695.J Bacteriol. 2002 Aug;184(16):4582-93. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.16.4582-4593.2002. J Bacteriol. 2002. PMID: 12142428 Free PMC article.
-
An expanded genome-scale model of Escherichia coli K-12 (iJR904 GSM/GPR).Genome Biol. 2003;4(9):R54. doi: 10.1186/gb-2003-4-9-r54. Epub 2003 Aug 28. Genome Biol. 2003. PMID: 12952533 Free PMC article.
-
Twin-arginine translocation system in Helicobacter pylori: TatC, but not TatB, is essential for viability.mBio. 2014 Jan 21;5(1):e01016-13. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01016-13. mBio. 2014. PMID: 24449753 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolism and genetics of Helicobacter pylori: the genome era.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 1999 Sep;63(3):642-74. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.63.3.642-674.1999. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 1999. PMID: 10477311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomics of Helicobacter pylori.Helicobacter. 2002;7 Suppl 1:1-7. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-5378.7.s1.1.x. Helicobacter. 2002. PMID: 12197903 Review.
Cited by
-
A systems biology approach to drug targets in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e34337. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034337. Epub 2012 Apr 16. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22523548 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic network model of a human oral pathogen.J Bacteriol. 2009 Jan;191(1):74-90. doi: 10.1128/JB.01123-08. Epub 2008 Oct 17. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 18931137 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing nature's toolbox: regulatory elements for synthetic biology.J R Soc Interface. 2009 Aug 6;6 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):S535-46. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2008.0521.focus. Epub 2009 Mar 4. J R Soc Interface. 2009. PMID: 19324675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-level transcription data of Yersinia pestis analyzed with a new metabolic constraint-based approach.BMC Syst Biol. 2012 Dec 6;6:150. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-6-150. BMC Syst Biol. 2012. PMID: 23216785 Free PMC article.
-
A genome-scale metabolic reconstruction of Pseudomonas putida KT2440: iJN746 as a cell factory.BMC Syst Biol. 2008 Sep 16;2:79. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-2-79. BMC Syst Biol. 2008. PMID: 18793442 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burns, B. P., S. L. Hazell, G. L. Mendz, T. Kolesnikow, D. Tillet, and B. A. Neilan. 2000. The Helicobacter pylori pyrB gene encoding aspartate carbamoyltransferase is essential for bacterial survival. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 380:78-84. - PubMed
-
- Chalker, A. F., H. W. Minehart, N. J. Hughes, K. K. Koretke, M. A. Lonetto, K. K. Brinkman, P. V. Warren, A. Lupas, M. J. Stanhope, J. R. Brown, and P. S. Hoffman. 2001. Systematic identification of selective essential genes in Helicobacter pylori by genome prioritization and allelic replacement mutagenesis. J. Bacteriol. 183:1259-1268. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chevalier, C., J. M. Thiberge, R. L. Ferrero, and A. Labigne. 1999. Essential role of Helicobacter pylori gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase for the colonization of the gastric mucosa of mice. Mol. Microbiol. 31:1359-1372. - PubMed
-
- Chirica, L. C., C. Petersson, M. Hurtig, B. H. Jonsson, T. Boren, and S. Lindskog. 2002. Expression and localization of alpha- and beta-carbonic anhydrase in Helicobacter pylori. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1601:192-199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

