Rapid in vivo Taxotere quantitative chemosensitivity response by 4.23 Tesla sodium MRI and histo-immunostaining features in N-Methyl-N-Nitrosourea induced breast tumors in rats
- PMID: 16078994
- PMCID: PMC1208921
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2867-5-26
Rapid in vivo Taxotere quantitative chemosensitivity response by 4.23 Tesla sodium MRI and histo-immunostaining features in N-Methyl-N-Nitrosourea induced breast tumors in rats
Abstract
Background: Sodium weighted images can indicate sodium signal intensities from different features in the tumor before and 24 hours following administration of Taxotere.
Aim: To evaluate the association of in vivo intracellular sodium magnetic resonance image intensities with immuno-biomarkers and histopathological features to monitor the early tumor response to Taxotere chemotherapy in Methyl-Nitroso-Urea induced rat xenograft breast tumors.
Methods and materials: Methyl-Nitroso-Urea (MNU) induced rat xenograft breast tumors were imaged for sodium MRI and compared with tumor histology, immunostaining after 24 hours chemotherapy.
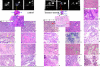
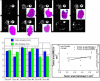
Results: Sodium MRI signal intensities represented sodium concentrations. Excised tumor histological sections showed different in vitro histological end points i.e. single strand DNA content of cell nuclei during cell cycle (G1/S-G2/M), distinct S or M histograms (Feulgen labeling to nuclear DNA content by CAS 200), mitotic figures and apoptosis at different locations of breast tumors. Necrosis and cystic fluid appeared gray on intracellular (IC) sodium images while apoptosis rich regions appeared brighter on IC sodium images. After 24 hours Taxotere-treated tumors showed lower 'IC/EC ratio' of viable cells (65-76%) with higher mitotic index; apoptotic tumor cells at high risk due to cytotoxicity (>70% with high apoptotic index); reduced proliferation index (270 vs 120 per high power field) associated with enhanced IC sodium in vivo MR image intensities and decreased tumor size (3%; p < 0.001; n = 16) than that of pre-treated tumors. IC-Na MR signal intensities possibly indicated Taxotere chemosensitivity response in vivo associated with apoptosis and different pre-malignant features within 24 hours of exposure of cancer cells to anti-neoplastic Taxotere drug.
Conclusion: Sodium MRI imaging may be used as in vivo rapid drug monitoring method to evaluate Taxotere chemosensitivity response associated with neoplasia, apoptosis and tumor histology features.
Figures
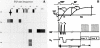






Similar articles
-
Taxotere chemosensitivity evaluation in mice prostate tumor: validation and diagnostic accuracy of quantitative measurement of tumor characteristics by MRI, PET, and histology of mice tumor.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2008 Jun;7(3):175-85. doi: 10.1177/153303460800700303. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2008. PMID: 18473489
-
Rapid in vivo monitoring of chemotherapeutic response using weighted sodium magnetic resonance imaging.Clin Cancer Res. 2000 Jun;6(6):2146-56. Clin Cancer Res. 2000. PMID: 10873063
-
Upregulating MMP-1 in carcinoma-associated fibroblasts reduces the efficacy of Taxotere on breast cancer synergized by Collagen IV.Oncol Lett. 2018 Sep;16(3):3537-3544. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.9092. Epub 2018 Jul 5. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30127959 Free PMC article.
-
Docetaxel-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles suppress breast cancer cells growth with reduced myelosuppression toxicity.Int J Nanomedicine. 2014 Oct 17;9:4829-46. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S70919. eCollection 2014. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014. PMID: 25378924 Free PMC article.
-
Final report on the safety assessment of capsicum annuum extract, capsicum annuum fruit extract, capsicum annuum resin, capsicum annuum fruit powder, capsicum frutescens fruit, capsicum frutescens fruit extract, capsicum frutescens resin, and capsaicin.Int J Toxicol. 2007;26 Suppl 1:3-106. doi: 10.1080/10915810601163939. Int J Toxicol. 2007. PMID: 17365137 Review.
Cited by
-
Morin augments anticarcinogenic and antiproliferative efficacy against 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)-anthracene induced experimental mammary carcinogenesis.Mol Cell Biochem. 2012 May;364(1-2):79-92. doi: 10.1007/s11010-011-1207-5. Epub 2012 Feb 19. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22350814
-
23 Na-MRI as a Noninvasive Biomarker for Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2021 Apr;53(4):995-1014. doi: 10.1002/jmri.27147. Epub 2020 Mar 26. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2021. PMID: 32219933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
17α-ethynyl-5α-androstane-3α, 17β-diol treatment of MNU-induced mammary cancer in rats.Int J Breast Cancer. 2011;2011:618757. doi: 10.4061/2011/618757. Epub 2011 Feb 14. Int J Breast Cancer. 2011. PMID: 22332014 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative sodium MR imaging and sodium bioscales for the management of brain tumors.Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2009 Nov;19(4):615-24. doi: 10.1016/j.nic.2009.09.001. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2009. PMID: 19959008 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium and proton diffusion MRI as biomarkers for early therapeutic response in subcutaneous tumors.Magn Reson Imaging. 2006 Apr;24(3):273-8. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2005.12.004. Epub 2006 Jan 26. Magn Reson Imaging. 2006. PMID: 16563956 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boada FE, Shen GX, Chang SY, Thulborn KR. Spectrally weighted twisted projection imaging: reducing T2 signal attenuation effects in fast three-dimensional sodium imaging. Magn Reson Med. 1997;38:1022–1028. - PubMed
-
- Ouwerkerk R, Bleich KB, Gillen JS, Pomper MG, Bottomley PA. Tissue sodium concentration in human brain tumors as measured with 23Na MR imaging. Radiology. 2003;227:529–537. - PubMed
-
- Kline R, Wu EX, Petrylak DP, Szabolcs M, Alderson PO, Weisfeldt ML, Cannon PJ, Katz J. Rapid in vivo monitoring of chemotherapeutic response using weighted sodium magnetic resonance imaging. Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6:2146–2156. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

