Active Nercc1 protein kinase concentrates at centrosomes early in mitosis and is necessary for proper spindle assembly
- PMID: 16079175
- PMCID: PMC1237086
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e05-04-0315
Active Nercc1 protein kinase concentrates at centrosomes early in mitosis and is necessary for proper spindle assembly
Abstract
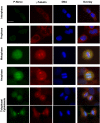
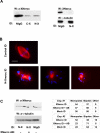
The Nercc1 protein kinase autoactivates in vitro and is activated in vivo during mitosis. Autoactivation in vitro requires phosphorylation of the activation loop at threonine 210. Mitotic activation of Nercc1 in mammalian cells is accompanied by Thr210 phosphorylation and involves a small fraction of total Nercc1. Mammalian Nercc1 coimmunoprecipitates gamma-tubulin and the activated Nercc1 polypeptides localize to the centrosomes and spindle poles during early mitosis, suggesting that active Nercc has important functions at the microtubular organizing center during cell division. To test this hypothesis, we characterized the Xenopus Nercc1 orthologue (XNercc). XNercc endogenous to meiotic egg extracts coprecipitates a multiprotein complex that contains gamma-tubulin and several components of the gamma-tubulin ring complex and localizes to the poles of spindles formed in vitro. Reciprocally, immunoprecipitates of the gamma-tubulin ring complex polypeptide Xgrip109 contain XNercc. Immunodepletion of XNercc from egg extracts results in delayed spindle assembly, fewer bipolar spindles, and the appearance of aberrant microtubule structures, aberrations corrected by addition of purified recombinant XNercc. XNercc immunodepletion also slows aster assembly induced by Ran-GTP, producing Ran-asters of abnormal size and morphology. Thus, Nercc1 contributes to both the centrosomal and the chromatin/Ran pathways that collaborate in the organization of a bipolar spindle.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Mitosis-specific anchoring of gamma tubulin complexes by pericentrin controls spindle organization and mitotic entry.Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Aug;15(8):3642-57. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e03-11-0796. Epub 2004 May 14. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15146056 Free PMC article.
-
The sequential activation of the mitotic microtubule assembly pathways favors bipolar spindle formation.Mol Biol Cell. 2016 Oct 1;27(19):2935-45. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E16-05-0322. Epub 2016 Aug 3. Mol Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27489339 Free PMC article.
-
Subgroup II PAK-mediated phosphorylation regulates Ran activity during mitosis.J Cell Biol. 2010 Sep 6;190(5):807-22. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200912056. Epub 2010 Aug 30. J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20805321 Free PMC article.
-
The role of mitotic kinases in coupling the centrosome cycle with the assembly of the mitotic spindle.J Cell Sci. 2014 Oct 1;127(Pt 19):4111-22. doi: 10.1242/jcs.151753. Epub 2014 Aug 15. J Cell Sci. 2014. PMID: 25128564 Review.
-
Spatial control of mitosis by the GTPase Ran.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007 Aug;64(15):1891-914. doi: 10.1007/s00018-007-6568-2. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007. PMID: 17483873 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In Mitosis You Are Not: The NIMA Family of Kinases in Aspergillus, Yeast, and Mammals.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 6;23(7):4041. doi: 10.3390/ijms23074041. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cdk1, Plks, Auroras, and Neks: the mitotic bodyguards.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;617:41-56. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-69080-3_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 18497029 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Recognition of host proteins by Helicobacter cysteine-rich protein C.Curr Microbiol. 2011 Sep;63(3):239-49. doi: 10.1007/s00284-011-9969-2. Epub 2011 Jul 7. Curr Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21735226
-
Cell cycle regulation by the NEK family of protein kinases.J Cell Sci. 2012 Oct 1;125(Pt 19):4423-33. doi: 10.1242/jcs.111195. Epub 2012 Nov 6. J Cell Sci. 2012. PMID: 23132929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel mutation causing nephronophthisis in the Lewis polycystic kidney rat localises to a conserved RCC1 domain in Nek8.BMC Genomics. 2012 Aug 16;13:393. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-393. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22899815 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Belham, C., Roig, J., Caldwell, J. A., Aoyama, Y., Kemp, B. E., Comb, M., and Avruch, J. (2003). A mitotic cascade of NIMA family kinases. Nercc1/Nek9 activates the Nek6 and Nek7 kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 34897-34909. - PubMed
-
- Carazo-Salas, R. E., Guarguaglini, G., Gruss, O. J., Segref, A., Karsenti, E., and Mattaj, I. W. (1999). Generation of GTP-bound Ran by RCC1 is required for chromatin-induced mitotic spindle formation. Nature 400, 178-181. - PubMed
-
- Desai, A., Murray, A., Mitchison, T. J., and Walczak, C. E. (1999). The use of Xenopus egg extracts to study mitotic spindle assembly and function in vitro. Methods Cell Biol. 61, 385-412. - PubMed
-
- Doxsey, S. (2001). Re-evaluating centrosome function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2, 688-698. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

