A genetic screen targeting the tumor necrosis factor/Eiger signaling pathway: identification of Drosophila TAB2 as a functionally conserved component
- PMID: 16079232
- PMCID: PMC1456095
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.105.045534
A genetic screen targeting the tumor necrosis factor/Eiger signaling pathway: identification of Drosophila TAB2 as a functionally conserved component
Abstract
Signaling by tumor necrosis factors (TNFs) plays a prominent role in mammalian development and disease. To fully understand this complex signaling pathway it is important to identify all regulators and transduction components. A single TNF family member, Eiger, is encoded in the Drosophila genome, offering the possibility of applying genetic approaches for pursuing this goal. Here we present a screen for the isolation of novel genes involved in the TNF/Eiger pathway. On the basis of Eiger's ability to potently activate Jun-N-terminal kinase (JNK) and trigger apoptosis, we used the Drosophila eye to establish an assay for dominant suppressors of this activity. In a large-scale screen the Drosophila homolog of TAB2/3 (dTAB2) was identified as an essential component of the Eiger-JNK pathway. Genetic epistasis and biochemical protein-protein interaction assays assign an adaptor role to dTAB2, linking dTRAF1 to the JNKKK dTAK1, demonstrating a conserved mechanism of TNF signal transduction in mammals and Drosophila. Thus, in contrast to morphogenetic processes, such as dorsal closure of the embryo, in which the JNK pathway is activated by the JNKKK Slipper, Eiger uses the dTAB2-dTAK1 module to induce JNK signaling activity.
Figures




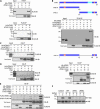
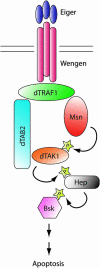
References
-
- Adachi-Yamada, T., K. Fujimura-Kamada, Y. Nishida and K. Matsumoto, 1999. Distortion of proximodistal information causes JNK-dependent apoptosis in Drosophila wing. Nature 400: 166–169. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner, M., 1989. Drosophila. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
-
- Basler, K., and G. Struhl, 1994. Compartment boundaries and the control of Drosophila limb pattern by hedgehog protein. Nature 368: 208–214. - PubMed
-
- Boutros, M., H. Agaisse and N. Perrimon, 2002. Sequential activation of signaling pathways during innate immune responses in Drosophila. Dev. Cell 3: 711–722. - PubMed
-
- Bradley, P. L., and D. J. Andrew, 2001. ribbon encodes a novel BTB/POZ protein required for directed cell migration in Drosophila melanogaster. Development 128: 3001–3015. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

