Correlation of bFGF expression in renal cell cancer with clinical and histopathological features by tissue microarray analysis and measurement of serum levels
- PMID: 16080018
- PMCID: PMC12161191
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-005-0019-y
Correlation of bFGF expression in renal cell cancer with clinical and histopathological features by tissue microarray analysis and measurement of serum levels
Abstract
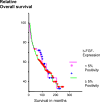
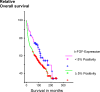
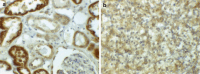
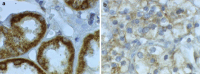
The prognostic value of bFGF for surgically treated renal cell cancer (RCC) patients was evaluated by immunohistochemistry (IHC) and the tissue microarray technique (TMA). Additionally, preoperative serum bFGF levels were correlated to tumour stage and the presence of metastases at initial diagnosis. Serum levels of bFGF were measured by ELISA in 39 healthy volunteers, in 37 patients with benign urologic diseases and in 74 RCC patients, 26 of whom revealed lymph node or distant metastases. bFGF expression as detected by IHC was investigated in 777 tissue cores from 259 different RCC patients [median follow-up: 138 (36-240) months]. Eighty eight patients died from tumour progression. For each patient, the TMA slides contained a tissue core from the primary tumour, its invasion front and the normal renal parenchyma. bFGF serum levels were higher in RCC patients vs healthy volunteers (P<0.01) and vs patients with benign urologic diseases (P<0.01). Metastasized patients revealed higher bFGF serum levels than organ-confined specimens (P<0.01). As detected by IHC only increased bFGF expression in the invasion front tissue correlated with the patients' long-term survival (log rank test) (P=0.03). In multivariate analysis regional LN metastases (P<0.01), the histological grading (P<0.01), and an increased bFGF expression in the invasion front (P=0.04) independently predicted the patients' clinical prognosis. Not the expression of bFGF in the primary tumour but in its invasion front reflects the aggressiveness of RCC, hereby indicating a different biological potential within both areas. The value of bFGF serum levels as indicators of systemic tumour dissemination remains to be determined.
Figures
Similar articles
-
mTOR and mTOR phosphorylation status in primary and metastatic renal cell carcinoma tissue: differential expression and clinical relevance.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019 Jan;145(1):153-163. doi: 10.1007/s00432-018-2775-5. Epub 2018 Oct 27. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30368665 Free PMC article.
-
Lack of TMEM27 expression is associated with postoperative progression of clinically localized conventional renal cell carcinoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2016 Sep;142(9):1947-53. doi: 10.1007/s00432-016-2207-3. Epub 2016 Jul 14. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27417314 Free PMC article.
-
Are Current Survival Prediction Tools Useful When Treating Subsequent Skeletal-related Events From Bone Metastases?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Sep 1;482(9):1710-1721. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003030. Epub 2024 Mar 22. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 38517402
-
Immunotherapy for advanced renal cell cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jan 25;(1):CD001425. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001425.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Dec 29;(12):CD001425. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001425.pub3. PMID: 15674877 Updated.
-
The role of c-Met in prognosis and clinicopathology of renal cell carcinoma: Results from a single-centre study and systematic review.Urol Oncol. 2017 Aug;35(8):532.e15-532.e23. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2017.03.027. Epub 2017 Apr 18. Urol Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28427859
Cited by
-
Expression of growth factors and their receptors in the primary renal cell carcinoma: new data and review.Cent European J Urol. 2020;73(4):466-475. doi: 10.5173/ceju.0189.R1. Epub 2020 Dec 9. Cent European J Urol. 2020. PMID: 33552572 Free PMC article.
-
The -553 T/A polymorphism in the promoter region of the FGF2 gene is associated with increased breast cancer risk in Polish women.Arch Med Sci. 2015 Jun 19;11(3):619-27. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2013.35996. Epub 2014 Jan 23. Arch Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26170857 Free PMC article.
-
Basic research in kidney cancer.Eur Urol. 2011 Oct;60(4):622-33. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2011.06.048. Epub 2011 Jul 5. Eur Urol. 2011. PMID: 21741760 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunochemical expression of fibroblast growth factor and its receptors in primary tumor cells of renal cell carcinoma.Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2021 Feb 15;9(1):65-72. eCollection 2021. Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2021. PMID: 33816695 Free PMC article.
-
A novel decoy receptor fusion protein for FGF-2 potently inhibits tumour growth.Br J Cancer. 2014 Jul 8;111(1):68-77. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2014.282. Epub 2014 May 29. Br J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24874473 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bichler KH, Wechsel HW (1999) The problematic nature of metastasized renal cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res 19:1463–1466 - PubMed
-
- Chodak GW, Hospelhorn V, Judge SM, Mayforth R, Koeppen H, Sasse J (1988) Increased levels of fibroblast growth factor-like activity in urine from patients with bladder or kidney cancer. Cancer Res 48(8):2083–2088 - PubMed
-
- Cronauer MV, Schulz WA, Seifert HH, Ackermann R, Burchardt M (2003) Fibroblast growth factors and their receptors in urological cancers: basic research and clinical implications. Eur Urol 43:309–319 - PubMed
-
- Dosquet C, Coudert MC, Lepage E, Cabane J, Richard F (1997) Are angiogenic factors, cytokines, and soluble adhesion molecules prognostic factors in patients with renal cell carcinoma? Clin Cancer Res 3:2451–2458 - PubMed
-
- Duensing S, Grosse J, Atzpodien J (1995) Increased serum levels of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) are associated with progressive lung metastases in advanced renal cell carcinoma patients. Anticancer Res 15:2331–2333 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

