Genomewide linkage study in 1,176 affected sister pair families identifies a significant susceptibility locus for endometriosis on chromosome 10q26
- PMID: 16080113
- PMCID: PMC1226203
- DOI: 10.1086/432960
Genomewide linkage study in 1,176 affected sister pair families identifies a significant susceptibility locus for endometriosis on chromosome 10q26
Abstract
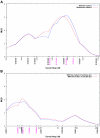
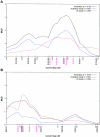
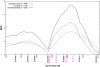
Endometriosis is a common gynecological disease that affects up to 10% of women in their reproductive years. It causes pelvic pain, severe dysmenorrhea, and subfertility. The disease is defined as the presence of tissue resembling endometrium in sites outside the uterus. Its cause remains uncertain despite >50 years of hypothesis-driven research, and thus the therapeutic options are limited. Disease predisposition is inherited as a complex genetic trait, which provides an alternative route to understanding the disease. We seek to identify susceptibility loci, using a positional-cloning approach that starts with linkage analysis to identify genomic regions likely to harbor these genes. We conducted a linkage study of 1,176 families (931 from an Australian group and 245 from a U.K. group), each with at least two members--mainly affected sister pairs--with surgically diagnosed disease. We have identified a region of significant linkage on chromosome 10q26 (maximum LOD score [MLS] of 3.09; genomewide P = .047) and another region of suggestive linkage on chromosome 20p13 (MLS = 2.09). Minor peaks (with MLS > 1.0) were found on chromosomes 2, 6, 7, 8, 12, 14, 15, and 17. This is the first report of linkage to a major locus for endometriosis. The findings will facilitate discovery of novel positional genetic variants that influence the risk of developing this debilitating disease. Greater understanding of the aberrant cellular and molecular mechanisms involved in the etiology and pathophysiology of endometriosis should lead to better diagnostic methods and targeted treatments.
Figures

References
Web Resources
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for endometriosis, EMX2, GALT, and PTEN)
References
-
- Abecasis GR, Burt RA, Hall D, Bochum S, Doheny KF, Lundy SL, Torrington M, Roos JL, Gogos JA, Karayiorgou M (2004a) Genomewide scan in families with schizophrenia from the founder population of Afrikaners reveals evidence for linkage and uniparental disomy on chromosome 1. Am J Hum Genet 74:403–417 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abecasis GR, Cherny SS, Cookson WO, Cardon LR (2001) GRR: graphical representation of relationship errors. Bioinformatics 17:742–743 - PubMed
-
- ——— (2002) Merlin—rapid analysis of dense genetic maps using sparse gene flow trees. Nat Genet 30:97–101 - PubMed
-
- Abecasis GR, Yashar BM, Zhao Y, Ghiasvand NM, Zareparsi S, Branham KE, Reddick AC, Trager EH, Yoshida S, Bahling J, Filippova E, Elner S, Johnson MW, Vine AK, Sieving PA, Jacobson SG, Richards JE, Swaroop A (2004b) Age-related macular degeneration: a high-resolution genome scan for susceptibility loci in a population enriched for late-stage disease. Am J Hum Genet 74:482–494 - PMC - PubMed
-
- American Fertility Society (1985) Revised American Fertility Society classification of endometriosis: 1985. Fertil Steril 43:351–352 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

