Susceptibility genes for age-related maculopathy on chromosome 10q26
- PMID: 16080115
- PMCID: PMC1226205
- DOI: 10.1086/444437
Susceptibility genes for age-related maculopathy on chromosome 10q26
Abstract
On the basis of genomewide linkage studies of families affected with age-related maculopathy (ARM), we previously identified a significant linkage peak on 10q26, which has been independently replicated by several groups. We performed a focused SNP genotyping study of our families and an additional control cohort. We identified a strong association signal overlying three genes, PLEKHA1, LOC387715, and PRSS11. All nonsynonymous SNPs in this critical region were genotyped, yielding a highly significant association (P < .00001) between PLEKHA1/LOC387715 and ARM. Although it is difficult to determine statistically which of these two genes is most important, SNPs in PLEKHA1 are more likely to account for the linkage signal in this region than are SNPs in LOC387715; thus, this gene and its alleles are implicated as an important risk factor for ARM. We also found weaker evidence supporting the possible involvement of the GRK5/RGS10 locus in ARM. These associations appear to be independent of the association of ARM with the Y402H allele of complement factor H, which has previously been reported as a major susceptibility factor for ARM. The combination of our analyses strongly implicates PLEKHA1/LOC387715 as primarily responsible for the evidence of linkage of ARM to the 10q26 locus and as a major contributor to ARM susceptibility. The association of either a single or a double copy of the high-risk allele within the PLEKHA1/LOC387715 locus accounts for an odds ratio of 5.0 (95% confidence interval 3.2-7.9) for ARM and a population attributable risk as high as 57%.
Figures

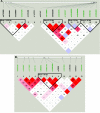

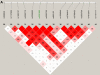






References
Web Resources
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for ARMD-1, CFH, PLEKHA1, PRSS11, GRK5, and RGS10)
-
- Division of Statistical Genetics, http://watson.hgen.pitt.edu/ (for Mega2)
-
- The R Project for Statistical Computing, http://www.r-project.org/ (for R statistical software)
References
-
- Abecasis GR, Cherny SS, Cookson WO, Cardon LR (2002) Merlin—rapid analysis of dense genetic maps using sparse gene flow trees. Nat Genet 30:97–101 - PubMed
-
- Abecasis GR, Yashar BM, Zhao Y, Ghiasvand NM, Zareparsi S, Branham KE, Reddick AC, Trager EH, Yoshida S, Bahling J, Filippova E, Elner S, Johnson MW, Vine AK, Sieving PA, Jacobson SG, Richards JE, Swaroop A (2004) Age-related macular degeneration: a high-resolution genome scan for susceptibility loci in a population enriched for late-stage disease. Am J Hum Genet 74:482–494 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ (2005) Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 21:263–265 - PubMed
-
- Browning SR, Briley JD, Briley LP, Chandra G, Charnecki JH, Ehm MG, Johansson KA, Jones BJ, Karter AJ, Yarnall DP, Wagner MJ (2005) Case-control single-marker and haplotypic association analysis of pedigree data. Genet Epidemiol 28:110–122 - PubMed
-
- Conley YP, Thalamuthu A, Jakobsdottir J, Weeks DE, Mah T, Ferrell RE, Gorin MB (2005) Candidate gene analysis suggests a role for fatty acid biosynthesis and regulation of the complement system in the etiology of age-related maculopathy. Hum Mol Genet 14:1991–2002 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

