Inhibitor-based methods for detection of plasmid-mediated AmpC beta-lactamases in Klebsiella spp., Escherichia coli, and Proteus mirabilis
- PMID: 16081966
- PMCID: PMC1233913
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.43.8.4163-4167.2005
Inhibitor-based methods for detection of plasmid-mediated AmpC beta-lactamases in Klebsiella spp., Escherichia coli, and Proteus mirabilis
Abstract
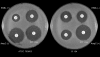
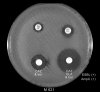
Non-beta-lactam inhibitor-based methods were evaluated for detecting plasmid-mediated AmpC beta-lactamases in Klebsiella spp., Escherichia coli, and Proteus mirabilis. Using CLSI methodology and disks containing cefotetan alone and in combination with 400 mug of boronic acid, 9 of 10 positive control strains and 54 of 55 AmpC-PCR-positive clinical isolates were detected. Importantly 71% and 40% of these clinical isolates were susceptible by routine testing to ceftriaxone and ceftazidime, respectively. Boronic acid disks also enhanced detection of expanded-spectrum beta-lactamases in AmpC producers.
Figures
References
-
- Bradford, P. A., C. Urban, N. Mariano, S. J. Projan, J. J. Rahal, and K. Bush. 1997. Imipenem resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae is associated with the combination of ACT-1, a plasmid-mediated AmpC β-lactamase, and the loss of an outer membrane protein. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 41:563-569. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Caroff, N., E. Espaze, D. Gautreau, H. Richet, and A. Reynaud. 2000. Analysis of the effects of -42 and -32 ampC promoter mutations in clinical isolates of Escherichia coli hyperproducing AmpC. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 45:783-788. - PubMed
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2005. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing: 15th informational supplement. M100-S15. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne. Pa.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

