Cholangiocyte endothelin 1 and transforming growth factor beta1 production in rat experimental hepatopulmonary syndrome
- PMID: 16083721
- PMCID: PMC2830806
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gastro.2005.05.050
Cholangiocyte endothelin 1 and transforming growth factor beta1 production in rat experimental hepatopulmonary syndrome
Abstract
Background & aims: Hepatic production and release of endothelin 1 plays a central role in experimental hepatopulmonary syndrome after common bile duct ligation by stimulating pulmonary endothelial nitric oxide production. In thioacetamide-induced nonbiliary cirrhosis, hepatic endothelin 1 production and release do not occur, and hepatopulmonary syndrome does not develop. However, the source and regulation of hepatic endothelin 1 after common bile duct ligation are not fully characterized. We evaluated the sources of hepatic endothelin 1 production after common bile duct ligation in relation to thioacetamide cirrhosis and assessed whether transforming growth factor beta1 regulates endothelin 1 production.
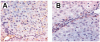
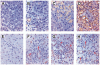
Methods: Hepatopulmonary syndrome and hepatic and plasma endothelin 1 levels were evaluated after common bile duct ligation or thioacetamide administration. Cellular sources of endothelin 1 were assessed by immunohistochemistry and laser capture microdissection of cholangiocytes. Transforming growth factor beta1 expression and signaling were assessed by using immunohistochemistry and Western blotting and by evaluating normal rat cholangiocytes.
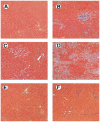
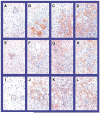
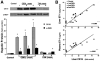
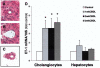
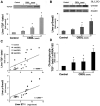
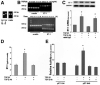
Results: Hepatic and plasma endothelin 1 levels increased and hepatopulmonary syndrome developed only after common bile duct ligation. Hepatic endothelin 1 and transforming growth factor beta1 levels increased over a similar time frame, and cholangiocytes were a major source of each peptide. Transforming growth factor beta1 signaling in cholangiocytes in vivo was evident by increased phosphorylation and nuclear localization of Smad2, and hepatic endothelin 1 levels correlated directly with liver transforming growth factor beta1 and phosphorylated Smad2 levels. Transforming growth factor beta1 also stimulated endothelin 1 promoter activity, expression, and production in normal rat cholangiocytes.
Conclusions: Cholangiocytes are a major source of hepatic endothelin 1 production during the development of hepatopulmonary syndrome after common bile duct ligation, but not in thioacetamide-induced cirrhosis. Transforming growth factor beta1 stimulates cholangiocyte endothelin 1 expression and production. Cholangiocyte-derived endothelin 1 may be an important endocrine mediator of experimental hepatopulmonary syndrome.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of receptor tyrosine kinase activation in cholangiocytes and pulmonary vascular endothelium in experimental hepatopulmonary syndrome.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014 Jan 1;306(1):G72-80. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00178.2013. Epub 2013 Nov 7. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24200956 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelin-1 in the rat bile duct ligation model of hepatopulmonary syndrome: correlation with pulmonary dysfunction.J Hepatol. 1998 Oct;29(4):571-8. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(98)80152-9. J Hepatol. 1998. PMID: 9824266
-
ET-1 and TNF-alpha in HPS: analysis in prehepatic portal hypertension and biliary and nonbiliary cirrhosis in rats.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2004 Feb;286(2):G294-303. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00298.2003. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2004. PMID: 14715521
-
Increased pulmonary vascular endothelin B receptor expression and responsiveness to endothelin-1 in cirrhotic and portal hypertensive rats: a potential mechanism in experimental hepatopulmonary syndrome.J Hepatol. 2003 May;38(5):556-63. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(03)00012-6. J Hepatol. 2003. PMID: 12713865
-
Mechanisms of pulmonary vascular complications of liver disease: hepatopulmonary syndrome.J Clin Gastroenterol. 2005 Apr;39(4 Suppl 2):S138-42. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 15758649 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of receptor tyrosine kinase activation in cholangiocytes and pulmonary vascular endothelium in experimental hepatopulmonary syndrome.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014 Jan 1;306(1):G72-80. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00178.2013. Epub 2013 Nov 7. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24200956 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular crosstalk during liver regeneration: unity in diversity.Cell Commun Signal. 2022 Aug 8;20(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-00918-z. Cell Commun Signal. 2022. PMID: 35941604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatopulmonary Syndrome.Dig Dis Sci. 2015 Jul;60(7):1914-23. doi: 10.1007/s10620-015-3593-0. Epub 2015 Mar 3. Dig Dis Sci. 2015. PMID: 25732713 Review.
-
Hepatopulmonary Syndrome and Liver Transplantation: A Recent Review of the Literature.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2016 Mar 28;4(1):47-53. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2015.00044. Epub 2016 Mar 15. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2016. PMID: 27047772 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pulmonary manifestations of chronic liver disease: a comprehensive review.Ann Gastroenterol. 2020 May-Jun;33(3):237-249. doi: 10.20524/aog.2020.0474. Epub 2020 Mar 27. Ann Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32382226 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fallon M, Abrams G. Pulmonary dysfunction in chronic liver disease. Hepatology. 2000;32:859–865. - PubMed
-
- Lange PA, Stoller JK. The hepatopulmonary syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1995;122:521–529. - PubMed
-
- Schenk P, Schoniger-Hekele M, Fuhrmann V, Madl C, Silberhumer G, Muller C. Prognostic significance of the hepatopulmonary syndrome in patients with cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2003;125:1042–1052. - PubMed
-
- Fallon MB, Abrams GA, Luo B, Hou Z, Dai J, Ku DD. The role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in the pathogenesis of a rat model of hepatopulmonary syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1997;113:606–614. - PubMed
-
- Carter EP, Hartsfield CL, Miyazono M, Jakkula M, Morris KG, Jr, McMurtry IF. Regulation of heme oxygenase-1 by nitric oxide during hepatopulmonary syndrome. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2002;283:L346–L353. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

