Halotolerant cyanobacterium Aphanothece halophytica contains NapA-type Na+/H+ antiporters with novel ion specificity that are involved in salt tolerance at alkaline pH
- PMID: 16085800
- PMCID: PMC1183346
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.71.8.4176-4184.2005
Halotolerant cyanobacterium Aphanothece halophytica contains NapA-type Na+/H+ antiporters with novel ion specificity that are involved in salt tolerance at alkaline pH
Abstract
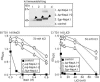
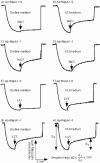
Aphanothece halophytica is a halotolerant alkaliphilic cyanobacterium which can grow at NaCl concentrations up to 3.0 M and at pH values up to 11. The genome sequence revealed that the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803 contains five putative Na+/H+ antiporters, two of which are homologous to NhaP of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and three of which are homologous to NapA of Enterococcus hirae. The physiological and functional properties of NapA-type antiporters are largely unknown. One of NapA-type antiporters in Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803 has been proposed to be essential for the survival of this organism. In this study, we examined the isolation and characterization of the homologous gene in Aphanothece halophytica. Two genes encoding polypeptides of the same size, designated Ap-napA1-1 and Ap-napA1-2, were isolated. Ap-NapA1-1 exhibited a higher level of homology to the Synechocystis ortholog (Syn-NapA1) than Ap-NapA1-2 exhibited. Ap-NapA1-1, Ap-NapA1-2, and Syn-NapA1 complemented the salt-sensitive phenotypes of an Escherichia coli mutant and exhibited strongly pH-dependent Na+/H+ and Li+/H+ exchange activities (the highest activities were at alkaline pH), although the activities of Ap-NapA1-2 were significantly lower than the activities of the other polypeptides. Only one these polypeptides, Ap-NapA1-2, complemented a K+ uptake-deficient E. coli mutant and exhibited K+ uptake activity. Mutagenesis experiments suggested the importance of Glu129, Asp225, and Asp226 in the putative transmembrane segment and Glu142 in the loop region for the activity. Overexpression of Ap-NapA1-1 in the freshwater cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942 enhanced the salt tolerance of cells, especially at alkaline pH. These findings indicate that A. halophytica has two NapA1-type antiporters which exhibit different ion specificities and play an important role in salt tolerance at alkaline pH.
Figures




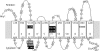
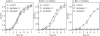

Similar articles
-
Halotolerant cyanobacterium Aphanothece halophytica contains an Na(+)/H(+) antiporter, homologous to eukaryotic ones, with novel ion specificity affected by C-terminal tail.J Biol Chem. 2001 Oct 5;276(40):36931-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M103650200. Epub 2001 Jul 30. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11479290
-
Isolation and functional characterization of Ca2+/H+ antiporters from cyanobacteria.J Biol Chem. 2004 Feb 6;279(6):4330-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M310282200. Epub 2003 Oct 14. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14559898
-
Halotolerant cyanobacterium Aphanothece halophytica contains a betaine transporter active at alkaline pH and high salinity.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006 Sep;72(9):6018-26. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00733-06. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16957224 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the biochemistry of the ubiquitous NhaP family of cation/H+ antiporters.Biochem Cell Biol. 2011 Apr;89(2):130-7. doi: 10.1139/o10-149. Biochem Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21455265 Review.
-
NhaA crystal structure: functional-structural insights.J Exp Biol. 2009 Jun;212(Pt 11):1593-603. doi: 10.1242/jeb.026708. J Exp Biol. 2009. PMID: 19448069 Review.
Cited by
-
Global transcriptional and circadian regulation in a halotolerant cyanobacterium Halothece sp. PCC7418.Sci Rep. 2022 Aug 12;12(1):13190. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17406-6. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35962002 Free PMC article.
-
Halotolerant cyanobacterium Aphanothece halophytica contains an Na+-dependent F1F0-ATP synthase with a potential role in salt-stress tolerance.J Biol Chem. 2011 Mar 25;286(12):10169-76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.208892. Epub 2011 Jan 24. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21262962 Free PMC article.
-
An Mrp-like cluster in the halotolerant cyanobacterium Aphanothece halophytica functions as a Na+/H+ antiporter.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009 Oct;75(20):6626-9. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01387-09. Epub 2009 Aug 21. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19700555 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Analysis of Gossypium hirsutum L. Reveals Different Mechanisms among NaCl, NaOH and Na2CO3 Stress Tolerance.Sci Rep. 2018 Sep 10;8(1):13527. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-31668-z. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30202076 Free PMC article.
-
Three putative cation/proton antiporters from the soda lake alkaliphile Alkalimonas amylolytica N10 complement an alkali-sensitive Escherichia coli mutant.Microbiology (Reading). 2007 Jul;153(Pt 7):2168-2179. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2007/007450-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2007. PMID: 17600061 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Apse, M. P., and E. Blumwald. 2002. Engineering salt tolerance in plants. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 13:146-150. - PubMed
-
- Elanskaya, I. V., I. V. Karandashova, A. V. Bogachev, and M. Hagemann. 2002. Functional analysis of the Na+/H+ antiporter encoding genes of the cyanobacterium Synechocystis PCC 6803. Biochemistry (Moscow) 67:432-440. - PubMed
-
- Hibino, T., N. Kaku, H. Yoshikawa, T. Takabe, and T. Takabe. 1999. Molecular characterization of DnaK from the halotolerant cyanobacterium Aphanothece halophytica for ATPase, protein folding, and copper binding under various salinity conditions. Plant Mol. Biol. 40:409-418. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

