Elucidation of a carotenoid biosynthesis gene cluster encoding a novel enzyme, 2,2'-beta-hydroxylase, from Brevundimonas sp. strain SD212 and combinatorial biosynthesis of new or rare xanthophylls
- PMID: 16085816
- PMCID: PMC1183362
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.71.8.4286-4296.2005
Elucidation of a carotenoid biosynthesis gene cluster encoding a novel enzyme, 2,2'-beta-hydroxylase, from Brevundimonas sp. strain SD212 and combinatorial biosynthesis of new or rare xanthophylls
Abstract
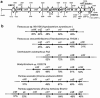
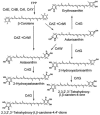
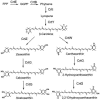
A carotenoid biosynthesis gene cluster mediating the production of 2-hydroxyastaxanthin was isolated from the marine bacterium Brevundimonas sp. strain SD212 by using a common crtI sequence as the probe DNA. A sequence analysis revealed this cluster to contain 12 open reading frames (ORFs), including the 7 known genes, crtW, crtY, crtI, crtB, crtE, idi, and crtZ. The individual ORFs were functionally analyzed by complementation studies using Escherichia coli that accumulated various carotenoid precursors due to the presence of other bacterial crt genes. In addition to functionally identifying the known crt genes, we found that one (ORF11, named crtG) coded for a novel enzyme, carotenoid 2,2'-beta-hydroxylase, which showed intriguingly partial homology with animal sterol-C5-desaturase. When this crtG gene was introduced into E. coli accumulating zeaxanthin and canthaxanthin, the resulting transformants produced their 2-hydroxylated and 2,2'-dihydroxylated products which were structurally novel or rare xanthophylls, as determined by their nuclear magnetic resonance and high-performance liquid chromatography/photodiode array detector/atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry spectral data. The new carotenoid produced was suggested to have a strong inhibitory effect on lipid peroxidation.
Figures

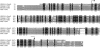
Similar articles
-
A carotenoid synthesis gene cluster from a non-marine Brevundimonas that synthesizes hydroxylated astaxanthin.Gene. 2006 Sep 1;379:101-8. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2006.04.017. Epub 2006 May 3. Gene. 2006. PMID: 16781830
-
Characterization of bacterial beta-carotene 3,3'-hydroxylases, CrtZ, and P450 in astaxanthin biosynthetic pathway and adonirubin production by gene combination in Escherichia coli.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2006 Oct;72(6):1238-46. doi: 10.1007/s00253-006-0426-2. Epub 2006 Apr 14. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2006. PMID: 16614859
-
Characterization of beta-carotene ketolases, CrtW, from marine bacteria by complementation analysis in Escherichia coli.Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2005 Sep-Oct;7(5):515-22. doi: 10.1007/s10126-004-5100-z. Epub 2005 Jul 5. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2005. PMID: 16007373
-
Carotenoid β-ring hydroxylase and ketolase from marine bacteria-promiscuous enzymes for synthesizing functional xanthophylls.Mar Drugs. 2011;9(5):757-771. doi: 10.3390/md9050757. Epub 2011 May 6. Mar Drugs. 2011. PMID: 21673887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress on molecular breeding and metabolic engineering of biosynthesis pathways of C(30), C(35), C(40), C(45), C(50) carotenoids.Biotechnol Adv. 2007 May-Jun;25(3):211-22. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2006.12.001. Epub 2006 Dec 19. Biotechnol Adv. 2007. PMID: 17257797 Review.
Cited by
-
When Carotenoid Biosynthesis Genes Met Escherichia coli : The Early Days and These Days.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1261:183-189. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-7360-6_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33783740
-
Cloning and characterization of genes involved in nostoxanthin biosynthesis of Sphingomonas elodea ATCC 31461.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35099. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035099. Epub 2012 Apr 11. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22509387 Free PMC article.
-
Combinatorial Biosynthesis of Novel Multi-Hydroxy Carotenoids in the Red Yeast Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous.J Fungi (Basel). 2017 Feb 22;3(1):9. doi: 10.3390/jof3010009. J Fungi (Basel). 2017. PMID: 29371528 Free PMC article.
-
Marine Microbial-Derived Resource Exploration: Uncovering the Hidden Potential of Marine Carotenoids.Mar Drugs. 2022 May 26;20(6):352. doi: 10.3390/md20060352. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35736155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differences in carotenoid composition among hymenobacter and related strains support a tree-like model of carotenoid evolution.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008 Apr;74(7):2016-22. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02306-07. Epub 2008 Feb 8. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18263749 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albrecht, M., N. Misawa, and G. Sandmann. 1999. Metabolic engineering of the terpenoid biosynthetic pathway of Escherichia coli for production of the carotenoids β-carotene and zeaxanthin. Biotechnol. Lett. 21:791-795.
-
- The Alpha-Tocopherol, Beta Carotene Cancer Prevention Study Group. 1994. The effect of vitamin E and β-carotene on the incidence of lung cancer and other cancers in male smokers. N. Engl. J. Med. 330:1029-1035. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong, G. A., and J. E. Hearst. 1996. Genetics and molecular biology of carotenoid pigment biosynthesis. FASEB J. 10:228-237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

