Use of Saccharomyces cerevisiae BLYES expressing bacterial bioluminescence for rapid, sensitive detection of estrogenic compounds
- PMID: 16085836
- PMCID: PMC1183329
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.71.8.4455-4460.2005
Use of Saccharomyces cerevisiae BLYES expressing bacterial bioluminescence for rapid, sensitive detection of estrogenic compounds
Abstract
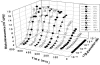
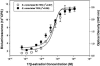
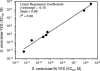
An estrogen-inducible bacterial lux-based bioluminescent reporter was developed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae for applications in chemical sensing and environmental assessment of estrogen disruptor activity. The strain, designated S. cerevisiae BLYES, was constructed by inserting tandem estrogen response elements between divergent yeast promoters GPD and ADH1 on pUTK401 (formerly pUA12B7) that constitutively express luxA and luxB to create pUTK407. Cotransformation of this plasmid with a second plasmid (pUTK404) containing the genes required for aldehyde synthesis (luxCDE) and FMN reduction (frp) yielded a bioluminescent bioreporter responsive to estrogen-disrupting compounds. For validation purposes, results with strain BLYES were compared to the colorimetric-based estrogenic assay that uses the yeast lacZ reporter strain (YES). Strains BLYES and YES were exposed to 17beta-estradiol over the concentration range of 1.2 x 10(-8) through 5.6 x 10(-12) M. Calculated 50% effective concentration values from the colorimetric and bioluminescence assays (n = 7) were similar at (4.4 +/- 1.1) x 10(-10) and (2.4 +/- 1.0) x 10(-10) M, respectively. The lower and upper limits of detection for each assay were also similar and were approximately 4.5 x 10(-11) to 2.8 x 10(-9) M. Bioluminescence was observed in as little as 1 h and reached its maximum in 6 h. In comparison, the YES assay required a minimum of 3 days for results. Strain BLYES fills the niche for rapid, high-throughput screening of estrogenic compounds and has the ability to be used for remote, near-real-time monitoring of estrogen-disrupting chemicals in the environment.
Figures

References
-
- Baker, V. A. 2001. Endocrine disrupters—testing strategies to assess human hazard. Toxicol. In Vitro 15:413-419. - PubMed
-
- Beresford, N., E. J. Routledge, C. A. Harris, and J. P. Sumpter. 2000. Issues arising when interpreting results from an in vitro assay for estrogenic activity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 162:22-33. - PubMed
-
- Bolton, E. K., G. S. Sayler, D. E. Nivens, J. M. Rochelle, S. Ripp, and M. L. Simpson. 2002. Integrated CMOS photodetectors and signal processing for very low-level chemical sensing with the bioluminescent bioreporter integrated circuit. Sens. Actuators B 85:179-185. - PubMed
-
- Cooper, R. L., and R. J. Kavlock. 1997. Endocrine disruptors and reproductive development: a weight-of-evidence overview. J. Endocrinol. 152:159-166. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

