Statistical analyses: possible reasons for unreliability of source tracking efforts
- PMID: 16085864
- PMCID: PMC1183283
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.71.8.4690-4695.2005
Statistical analyses: possible reasons for unreliability of source tracking efforts
Abstract
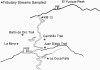
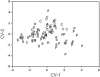
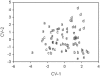
Analyses for the presence of indicator organisms provide information on the microbiological quality of water. Indicator organisms recommended by the United States Environmental Protection Agency for monitoring the microbiological quality of water include Escherichia coli, a thermotolerant coliform found in the feces of warm-blooded animals. These bacteria can also be isolated from environmental sources such as the recreational and pristine waters of tropical rain forests in the absence of fecal contamination. In the present study, E. coli isolates were compared to E. coli K12 (ATCC 29425) by restriction fragment length polymorphism using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Theoretically, genomic DNA patterns generated by PFGE are highly specific for the different isolates of an organism and can be used to identify variability between environmental and fecal isolates. Our results indicate a different band pattern for almost every one of the E. coli isolates analyzed. Cluster analysis did not show any relations between isolates and their source of origin. Only the discriminant function analysis grouped the samples with the source of origin. The discrepancy observed between the cluster analysis and discriminant function analysis relies on their mathematical basis. Our validation analyses indicate the presence of an artifact (i.e., grouping of environmental versus fecal samples as a product of the statistical analyses used and not as a result of separation in terms of source of origin) in the classification results; therefore, the large genetic heterogeneity observed in these E. coli populations makes the grouping of isolates by source rather difficult, if not impossible.
Figures

References
-
- American Public Health Association. 1988. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 17th ed. American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation, Washington, D.C.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 1997. Standardized molecular subtyping of Escherichia coli O157:H7 by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: a training manual. Foodborne and Diarrheal Diseases Branch, Division of Bacterial and Mycotic Diseases, National Center for Infectious Diseases, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, Ga.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

