Genomewide identification of Sko1 target promoters reveals a regulatory network that operates in response to osmotic stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 16087739
- PMCID: PMC1214534
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.4.8.1343-1352.2005
Genomewide identification of Sko1 target promoters reveals a regulatory network that operates in response to osmotic stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
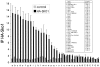
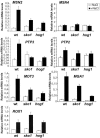
In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the ATF/CREB transcription factor Sko1 (Acr1) regulates the expression of genes induced by osmotic stress under the control of the high osmolarity glycerol (HOG) mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. By combining chromatin immunoprecipitation and microarrays containing essentially all intergenic regions, we estimate that yeast cells contain approximately 40 Sko1 target promoters in vivo; 20 Sko1 target promoters were validated by direct analysis of individual loci. The ATF/CREB consensus sequence is not statistically overrepresented in confirmed Sko1 target promoters, although some sites are evolutionarily conserved among related yeast species, suggesting that they are functionally important in vivo. These observations suggest that Sko1 association in vivo is affected by factors beyond the protein-DNA interaction defined in vitro. Sko1 binds a number of promoters for genes directly involved in defense functions that relieve osmotic stress. In addition, Sko1 binds to the promoters of genes encoding transcription factors, including Msn2, Mot3, Rox1, Mga1, and Gat2. Stress-induced expression of MSN2, MOT3, and MGA1 is diminished in sko1 mutant cells, while transcriptional regulation of ROX1 seems to be unaffected. Lastly, Sko1 targets PTP3, which encodes a phosphatase that negatively regulates Hog1 kinase activity, and Sko1 is required for osmotic induction of PTP3 expression. Taken together our results suggest that Sko1 operates a transcriptional network upon osmotic stress, which involves other specific transcription factors and a phosphatase that regulates the key component of the signal transduction pathway.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sumoylation of DNA-bound transcription factor Sko1 prevents its association with nontarget promoters.PLoS Genet. 2019 Feb 14;15(2):e1007991. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007991. eCollection 2019 Feb. PLoS Genet. 2019. PMID: 30763307 Free PMC article.
-
Hog1 kinase converts the Sko1-Cyc8-Tup1 repressor complex into an activator that recruits SAGA and SWI/SNF in response to osmotic stress.Mol Cell. 2002 Jun;9(6):1307-17. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00557-9. Mol Cell. 2002. PMID: 12086627
-
Regulation of the Sko1 transcriptional repressor by the Hog1 MAP kinase in response to osmotic stress.EMBO J. 2001 Mar 1;20(5):1123-33. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.5.1123. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11230135 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast go the whole HOG for the hyperosmotic response.Trends Genet. 2002 Aug;18(8):405-12. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(02)02723-3. Trends Genet. 2002. PMID: 12142009 Review.
-
Mechanisms for the epigenetic inheritance of stress response in single cells.Curr Genet. 2018 Dec;64(6):1221-1228. doi: 10.1007/s00294-018-0849-1. Epub 2018 May 30. Curr Genet. 2018. PMID: 29846762 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Activator and repressor functions of the Mot3 transcription factor in the osmostress response of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Eukaryot Cell. 2013 May;12(5):636-47. doi: 10.1128/EC.00037-13. Epub 2013 Feb 22. Eukaryot Cell. 2013. PMID: 23435728 Free PMC article.
-
An expanded cell wall damage signaling network is comprised of the transcription factors Rlm1 and Sko1 in Candida albicans.PLoS Genet. 2020 Jul 8;16(7):e1008908. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008908. eCollection 2020 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 32639995 Free PMC article.
-
Hog1-induced transcription of RTC3 and HSP12 is robust and occurs in cells lacking Msn2, Msn4, Hot1 and Sko1.PLoS One. 2020 Aug 17;15(8):e0237540. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237540. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32804965 Free PMC article.
-
Where does mediator bind in vivo?PLoS One. 2009;4(4):e5029. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005029. Epub 2009 Apr 3. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19343176 Free PMC article.
-
A chromatin-mediated mechanism for specification of conditional transcription factor targets.Nat Genet. 2006 Dec;38(12):1446-51. doi: 10.1038/ng1917. Epub 2006 Nov 12. Nat Genet. 2006. PMID: 17099712 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alepuz, M. P., A. Jovanovic, V. Reiser, and G. Ammerer. 2001. Stress-induced MAP kinase Hog1 is part of transcription activation complexes. Mol. Cell 7:767-777. - PubMed
-
- Bilsland, E., C. Molin, S. Swaminathan, A. Ramne, and P. Sunnerhagen. 2004. Rck1 and Rck2 MAPKAP kinases and the HOG pathway are required for oxidative stress resistance. Mol. Microbiol. 53:1743-1756. - PubMed
-
- Cawley, S., S. Bekiranov, H. H. Ng, P. Kapranov, E. A. Sekinger, D. Kampa, A. Piccolboni, V. Smentchenko, J. Cheng, A. J. Williams, R. Wheeler, B. Wong, J. Drenkow, M. Yamanaka, S. Patel, S. Brubaker, H. Tammana, G. Helt, K. Struhl, and T. R. Gingeras. 2004. Unbiased mapping of transcription factor binding sites along human chromosomes 21 and 22 points to widespread regulation of non-coding RNAs. Cell 116:499-509. - PubMed
-
- Cliften, P., P. Sudarsanam, A. Desikan, L. Fulton, B. Fulton, J. Majors, R. Waterston, B. A. Cohen, and M. Johnston. 2003. Finding functional features in Saccharomyces genomes by phylogenetic footprinting. Science 301:71-76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

