Orientation of human semicircular canals measured by three-dimensional multiplanar CT reconstruction
- PMID: 16088383
- PMCID: PMC2504595
- DOI: 10.1007/s10162-005-0003-x
Orientation of human semicircular canals measured by three-dimensional multiplanar CT reconstruction
Abstract
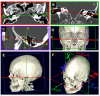
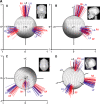
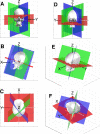
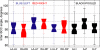
Analysis of vestibulo-ocular reflex experiments requires knowledge of the absolute orientations (with respect to skull landmarks) of semicircular canals (SCC). Data relating SCC orientations to accessible skull landmarks in humans are sparse, apart from a classic study of 10 skulls, which concluded that the horizontal and anterior SCC are not mutually orthogonal (111 +/- 7.6 degrees). Multiple studies of isolated labyrinths have shown the inter-SCC angles are close to 90 degrees. We hypothesized that a larger sample would yield mean absolute SCC orientations closer to the mutual orthogonality demonstrated for isolated labyrinths. We measured canal orientations with respect to accessible skull landmarks using 3-D multiplanar reconstructions of computerized tomography scans of the temporal bones of 22 human subjects. Images were acquired with 0.5-mm thickness and reconstructed with in-plane resolution of 234 microm. There was no significant difference between the left and a mirror image of the right (p > 0.57 on multiway ANOVA of orientation vector coefficients), so data were pooled for the 44 labyrinths. The angle between the anterior and posterior SCC was 94.0 +/- 4.0 degrees (mean +/- SD). The angle between the anterior and horizontal SCC was 90.6 +/- 6.2 degrees. The angle between the horizontal and posterior SCC was 90.4 +/- 4.9 degrees. The direction angles between a vector normal to the left horizontal SCC and the positive Reid's stereotaxic X (+nasal), Y (+left), and Z (+superior) axes were 108.7 +/- 7.5 degrees, 92.2 +/- 5.7 degrees, and 19.9 +/- 7.0 degrees, respectively. The angles between a vector normal to the left anterior SCC and the positive Reid's stereotaxic X, Y, and Z axes were 125.9 +/- 5.2 degrees, 38.4 +/- 5.1 degrees, and 100.1 +/- 6.2 degrees, respectively. The angles between a vector normal to the left posterior SCC and the positive Reid's stereotaxic X, Y, and Z axes were 133.6 +/- 5.3 degrees, 131.5 +/- 5.1 degrees, and 105.6 +/- 6.6 degrees, respectively. The mean anterior SCC-contralateral posterior SCC angle was 15.3 +/- 7.2 degrees. The absolute orientations of human SCC are more nearly orthogonal than previously reported.
Figures


References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '3263051', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3263051/'}]}
- Archer CR, Cooper MH, Kveton JF. Correlation of high-resolution computed tomography and gross anatomic sections of the temporal bone. II. Vestibular apparatus. Am. J. Otol. 9:276–281, 1988. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '8985897', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8985897/'}]}
- Aw ST, Halmagyi gm, Haslwanter T, Curthoys IS, Yavor RA, Todd MJ. Three-dimensional vector analysis of the human vestibuloocular reflex in response to high-acceleration head rotations. II. Responses in subjects with unilateral vestibular loss and selective semicircular canal occlusion. J. Neurophysiol. 76:4021–4030, 1996. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.3109/00016487509121318', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.3109/00016487509121318'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '1101636', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1101636/'}]}
- Blanks RH, Curthoys IS, Markham CH. Planar relationships of the semicircular canals in man. Acta Otolaryngol. 80:185–196, 1975. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.3109/00016489609137882', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.3109/00016489609137882'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '8831835', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8831835/'}]}
- Bohmer A, Straumann D, Suzuki J, Hess BJ, Henn V. Contributions of single semicircular canals to caloric nystagmus as revealed by canal plugging in rhesus monkeys. Acta Otolaryngol. 116(4):513–520, 1996. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '14128701', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14128701/'}]}
- Cohen B, Suzuki JI, Bender MB. Eye movements from semicircular canal nerve stimulation in the cat. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 73:153–169, 1964. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

