The shed ectodomain of type XIII collagen associates with the fibrillar fibronectin matrix and may interfere with its assembly in vitro
- PMID: 16091016
- PMCID: PMC1383662
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20051073
The shed ectodomain of type XIII collagen associates with the fibrillar fibronectin matrix and may interfere with its assembly in vitro
Abstract
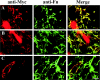
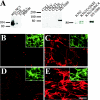
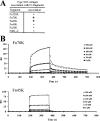
Type XIII collagen is a transmembrane collagen, which is known to exist also as a soluble variant due to ectodomain shedding. Earlier studies with the recombinant ectodomain have shown it to interact in vitro with a number of extracellular matrix proteins, e.g. Fn (fibronectin). In view of its strong binding to Fn, we examined in the present study whether the released soluble ectodomain can bind to the fibrillar Fn matrix under cell-culture conditions and, if so, influence its assembly. In this study, we demonstrate that the type XIII collagen ectodomain of mammalian cells can associate with Fn fibres and may eventually hamper incorporation of the fibrillar Fn meshwork. The association between type XIII collagen and Fn was implicated to be mediated by the C-terminal end of type XIII collagen and the N-terminal end of Fn. The results presented here imply that the shedding of the type XIII collagen ectodomain results in a biologically active molecule capable of remodelling the structure of the pericellular matrix.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Lack of cytosolic and transmembrane domains of type XIII collagen results in progressive myopathy.Am J Pathol. 2001 Oct;159(4):1581-92. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)62542-4. Am J Pathol. 2001. PMID: 11583983 Free PMC article.
-
The type XIII collagen ectodomain is a 150-nm rod and capable of binding to fibronectin, nidogen-2, perlecan, and heparin.J Biol Chem. 2002 Jun 21;277(25):23092-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M107583200. Epub 2002 Apr 15. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11956183
-
Differential regulation of fibronectin fibrillogenesis by protein kinases A and C.Connect Tissue Res. 2002;43(1):22-31. Connect Tissue Res. 2002. PMID: 12180265
-
Collagen XIII: a type II transmembrane protein with relevance to musculoskeletal tissues, microvessels and inflammation.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012 May;44(5):714-7. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2012.01.024. Epub 2012 Feb 8. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22342189 Review.
-
Roles of integrins in fibronectin matrix assembly.Histol Histopathol. 1997 Jan;12(1):233-40. Histol Histopathol. 1997. PMID: 9046058 Review.
Cited by
-
The CMS19 disease model specifies a pivotal role for collagen XIII in bone homeostasis.Sci Rep. 2022 Apr 7;12(1):5866. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-09653-4. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35393492 Free PMC article.
-
Muscle-derived collagen XIII regulates maturation of the skeletal neuromuscular junction.J Neurosci. 2010 Sep 15;30(37):12230-41. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5518-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20844119 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of collagen XIII to lung function and development of pulmonary fibrosis.BMJ Open Respir Res. 2023 Dec 12;10(1):e001850. doi: 10.1136/bmjresp-2023-001850. BMJ Open Respir Res. 2023. PMID: 38568728 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Geiger B., Bershadsky A., Pankov R., Yamada K. M. Transmembrane extracellular matrix-cytoskeleton crosstalk. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001;2:793–805. - PubMed
-
- Vu T. H. Don't mess with the matrix. Nat. Genet. 2001;28:202–203. - PubMed
-
- Kleinman H. K., Philp D., Hoffman M. P. Role of the extracellular matrix in morphogenesis. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2003;14:526–532. - PubMed
-
- Quaranta V., Giannelli G. Cancer invasion: watch your neighbourhood! Tumori. 2003;89:343–348. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

