Specific role for p85/p110beta in GTP-binding-protein-mediated activation of Akt
- PMID: 16091017
- PMCID: PMC1316301
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20050671
Specific role for p85/p110beta in GTP-binding-protein-mediated activation of Akt
Abstract
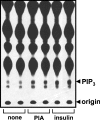
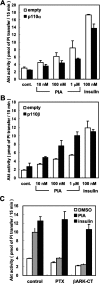
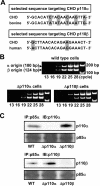
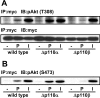
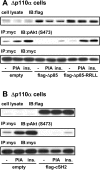
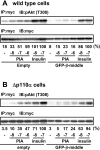
We prepared CHO (Chinese hamster ovary) cells expressing both IR (insulin receptor) and A1R (A1 adenosine receptor). Treatment of the cells with insulin or PIA [N6-(2-phenylisopropyl)adenosine], a specific A(1)R agonist increased Akt activity in the cells in a PI3K- (phosphoinositide 3-kinase) dependent manner. Transfection of p110beta into the cells augmented the action of PIA with little effect on insulin. Introduction of a pH1 vector producing shRNA (short hairpin RNA) that targets p110beta abolished PIA-induced Akt activation. By contrast, an shRNA probe targeting p110alpha did not impair the effects of PIA. The effect of PIA in p110alpha-deficient cells was attenuated effectively by both Deltap85 and betaARK-CT (beta-adrenergic receptor kinase-C-terminal peptide). A Deltap85-derived protein possessing point mutations in its two SH2 domains did not impair PIA action. These results suggest that tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins and Gbetagamma (betagamma subunits of GTP-binding protein) are necessary for the specific function of p110beta in intact cells. The p110beta-middle (middle part of p110beta) may play an important role in signal reception from GPCRs (GTP-binding-protein-coupled receptor), because transfection of the middle part impaired PIA sensitivity.
Figures
References
-
- Carpenter C. L., Auger K. R., Chanudhuri M., Yoakim M., Schaffhausen B., Shoelson S., Cantley L. C. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase is activated by phosphopeptides that bind to the SH2 domains of the 85-kDa subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 1993;268:9478–9483. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

