The alphaC domains of fibrinogen affect the structure of the fibrin clot, its physical properties, and its susceptibility to fibrinolysis
- PMID: 16091450
- PMCID: PMC1895112
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2005-05-2150
The alphaC domains of fibrinogen affect the structure of the fibrin clot, its physical properties, and its susceptibility to fibrinolysis
Abstract
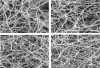
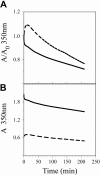
The functions of the alphaC domains of fibrinogen in clotting and fibrinolysis, which have long been enigmatic, were determined using recombinant fibrinogen truncated at Aalpha chain residue 251. Scanning electron microscopy and confocal microscopy revealed that the fibers of alpha251 clots were thinner and denser, with more branch points than fibers of control clots. Consistent with these results, the permeability of alpha251 clots was nearly half that of control clots. Together, these results suggest that in normal clot formation, the alphaC domains enhance lateral aggregation to produce thicker fibers. The viscoelastic properties of alpha251 fibrin clots differed markedly from control clots; alpha251 clots were much less stiff and showed more plastic deformation, indicating that interactions between the alphaC domains in normal clots play a major role in determining the clot's mechanical properties. Comparing factor XIIIa cross-linked alpha251 and control clots showed that gamma chain cross-linking had a significant effect on clot stiffness. Plasmin-catalyzed lysis of alpha251 clots, monitored with both macroscopic and microscopic methods, was faster than lysis of control clots. In conclusion, these studies provide the first definitive evidence that the alphaC domains play an important role in determining the structure and biophysical properties of clots and their susceptibility to fibrinolysis.
Figures



References
-
- Mosesson MW, Hainfeld J, Wall J, Haschemeyer RH. Identification and mass analysis of human fibrinogen molecules and their domains by scanning transmission electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1981;153: 695-718. - PubMed
-
- Medved LV, Gorkun OV, Privalov PL. Structural organization of C-terminal parts of fibrinogen A alpha-chains. FEBS Lett. 1983;160: 291-295. - PubMed
-
- Weisel JW, Stauffacher CV, Bullitt E, Cohen C. A model for fibrinogen: domains and sequence. Science. 1985;230: 1388-1391. - PubMed
-
- Weisel JW, Medved L. The structure and function of the alpha C domains of fibrinogen. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001;936: 312-327. - PubMed
-
- Veklich YI, Gorkun OV, Medved LV, Nieuwenhuizen W, Weisel JW. Carboxyl-terminal portions of the alpha chains of fibrinogen and fibrin: localization by electron microscopy and the effects of isolated alpha C fragments on polymerization. J Biol Chem. 1993;268: 13577-13585. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

