NKG2D-independent suppression of T cell proliferation by H60 and MICA
- PMID: 16091471
- PMCID: PMC1187963
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0502026102
NKG2D-independent suppression of T cell proliferation by H60 and MICA
Abstract
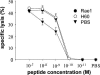
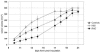
The activating receptor NKG2D recognizes a wide range of different ligands, some of which are primarily expressed in "stressed" tissues or on tumor cells. Until now, similar stimulatory effects on natural killer and CD8+ T cells have been described for all NKG2D ligands, and the NKG2D receptor/ligand system has therefore been interpreted as a sensor system involved in tumor immune surveillance and activation of immune responses. We show here that the NKG2D ligands H60 and MIC class 1 chain-related protein A (MICA) can also mediate strong suppressive effects on T cell proliferation. Responsiveness to H60- and MICA-mediated suppression requires IL-10 and involves a receptor other than NKG2D. These findings might provide explanations for the observation that strong in vivo NKG2D ligand expression, such as that on tumor cells, sometimes fails to support effective immune responses and links this observation to a distinct subgroup of NKG2D ligands.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Rae1 and H60 ligands of the NKG2D receptor stimulate tumour immunity.Nature. 2001 Sep 13;413(6852):165-71. doi: 10.1038/35093109. Nature. 2001. PMID: 11557981 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular competition for NKG2D: H60 and RAE1 compete unequally for NKG2D with dominance of H60.Immunity. 2001 Aug;15(2):201-11. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(01)00187-x. Immunity. 2001. PMID: 11520456
-
IFN-dependent down-regulation of the NKG2D ligand H60 on tumors.J Immunol. 2006 Jan 15;176(2):905-13. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.2.905. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16393975
-
Strategies for target cell recognition by natural killer cells.Immunol Rev. 2001 Jun;181:170-84. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-065x.2001.1810114.x. Immunol Rev. 2001. PMID: 11513138 Review.
-
UL16 binding proteins.Immunobiology. 2004;209(3):283-90. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2004.04.008. Immunobiology. 2004. PMID: 15518340 Review.
Cited by
-
The current state of knowledge on the role of NKG2D ligands in multiple sclerosis and other autoimmune diseases.Front Mol Neurosci. 2025 Jan 10;17:1493308. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2024.1493308. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39866909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Costimulation of dendritic epidermal gammadelta T cells by a new NKG2D ligand expressed specifically in the skin.J Immunol. 2009 Apr 15;182(8):4557-64. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0802439. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19342629 Free PMC article.
-
Proteasome regulation of ULBP1 transcription.J Immunol. 2009 May 15;182(10):6600-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0801214. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19414815 Free PMC article.
-
Altered expression of Raet1e, a major histocompatibility complex class 1-like molecule, underlies the atherosclerosis modifier locus Ath11 10b.Circ Res. 2013 Oct 12;113(9):1054-64. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.113.302052. Epub 2013 Aug 15. Circ Res. 2013. PMID: 23948654 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of serum MMP3 and other biomarkers with clinical outcomes in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a pilot study.Clin Rheumatol. 2017 Aug;36(8):1819-1826. doi: 10.1007/s10067-017-3624-7. Epub 2017 Apr 22. Clin Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 28432524
References
-
- Diefenbach, A. & Raulet, D. H. (2003) Curr. Opin. Immunol. 15, 37-44. - PubMed
-
- Ravetch, J. V. & Lanier, L. L. (2000) Science 290, 84-89. - PubMed
-
- Raulet, D. H. (2003) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 3, 781-790. - PubMed
-
- Wu, J., Song, Y., Bakker, A. B., Bauer, S., Spies, T., Lanier, L. L. & Phillips, J. H. (1999) Science 285, 730-732. - PubMed
-
- Bauer, S., Groh, V., Wu, J., Steinle, A., Phillips, J. H., Lanier, L. L. & Spies, T. (1999) Science 285, 727-729. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

