Thiamine deficiency in infants: MR findings in the brain
- PMID: 16091511
- PMCID: PMC7975150
Thiamine deficiency in infants: MR findings in the brain
Abstract
Background and purpose: Thiamine deficiency is extremely rare in infants in developed countries. To our knowledge, its MR findings in the brain have not been reported. The purpose of this study was to investigate the brain MR findings in infants with encephalopathy due to thiamine deficiency.
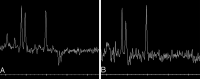
Methods: The study group included six infants aged 2-10 months with encephalopathy who had been fed with solely soy-based formula devoid of thiamine from birth. All underwent MR evaluation at admission and follow-up (total of 14 examinations). In one patient, MR spectroscopy (MRS) was performed.
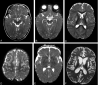
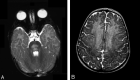
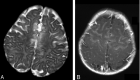
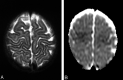
Results: In five patients T2-weighted, fluid-attenuated inversion recovery, or proton-attenuated sequences showed bilateral and symmetric hyperintensity in the periaqueductal area, basal ganglia and thalami. Five had lesions in the mammillary bodies, and three, in the brain stem. In all six patients, the frontal region (cortex and white matter) was clearly involved. At presentation, MRS of the periaqueductal area showed a lactate doublet. On long-term follow-up, three of four patients had severe frontal damage; in two, this occurred as part of diffuse parenchymal loss, and in one, it was accompanied by atrophy of the basal ganglia and thalami.
Conclusion: Thiamine deficiency in infants is characterized by involvement of the frontal lobes and basal ganglia, in addition to the lesions in the periaqueductal region, thalami, and the mammillary bodies described in adults. MRS demonstrates a characteristic lactate peak.
Figures
References
-
- Russell RM. Vitamin and trace mineral deficiency and excess. In: Harrison’s principles of internal medicine. 15th ed. New York: McGraw Hill;2001;461–464
-
- Jack CR, Lexa FJ, Trojanowski JQ, et al. Normal aging, dementia and neurodegenerative disease. In: Atlas SW, ed. Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain and spine. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins;2002. :1177–1240
-
- Vasconcelos MM, Silva KP, Vidal G, et al. Early diagnosis of pediatric Wernicke’s encephalopathy. Pediatr Neurol 1999;20:289–294 - PubMed
-
- Wyalt DT, Michael JN, Hillman RE. Infantile beriberi presenting as subacute necrotizing encephalomyelopathy. J Pediatr 1987;110:888–891 - PubMed
-
- Tanphaichit V. Thiamin. In: Shils ME, Olson JA, Shike M, Ross AC, eds. Modern nutrition in health and disease. 9th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins;1999;381–389
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
