mRNA expression and localization of bNOS, eNOS and iNOS in human cervix at preterm and term labour
- PMID: 16092967
- PMCID: PMC1188074
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7827-3-33
mRNA expression and localization of bNOS, eNOS and iNOS in human cervix at preterm and term labour
Abstract
Background: Preterm birth is the primary cause of the neonatal mortality and morbidity. There will be no preterm birth without a cervical softening. Nitric oxide (NO) is shown to be a mediator of term cervical ripening. The aim of this study was to investigate mRNA expression of the three isomers of NO synthases (NOS) and to identify them by immunohistochemistry in the human cervix at preterm birth compared to term.
Methods: The three isomers of NOS--inducible (iNOS), endothelial (eNOS) and neuronal (bNOS)--were investigated in the human cervix. The expression of mRNA was determined using Real-Time Multiplex RT-PCR. The localisation of synthases in the cervical tissue was analysed using immunohistochemistry. Cervical biopsies were obtained from 4 groups of women without clinical signs of infection: preterm (PTL), term labour (TL), preterm not in labour (PTnotL) and term not in labour (TnotL) patients. One-Way ANOVA, Kruskal-Wallis, Student t-test or Mann-Whitney test were applied as appropriate to determine statistically significant differences among the groups.
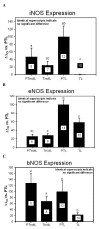
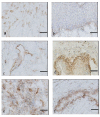
Results: Patients in preterm labour had significantly (p < 0.01) higher mRNA levels of all the three NOS isomers compared to those in term labour. Women not in labour, irrespective of gestational age, thus with unripe cervices, had significantly lower eNOS mRNA levels compared to those in labour (p < 0.01). Immunoreactivity for all three NO synthases was observed in each examined sample in all groups. The bNOS staining was the most prominent.
Conclusion: The mRNA levels were higher in the preterm labour group compared to the women at term labour. The significant increase of the eNOS mRNA expression, from the unripe to the favourable cervical state during labour, may indicate a role of eNOS and supports the role of NO in the cervical ripening process. All the three synthases were identified by immunohistochemistry in all the groups of study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Non-infected preterm parturition is related to increased concentrations of IL-6, IL-8 and MCP-1 in human cervix.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2005 Aug 25;3:39. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-3-39. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2005. PMID: 16122384 Free PMC article.
-
Corticotropin-releasing hormone, its binding protein and receptors in human cervical tissue at preterm and term labor in comparison to non-pregnant state.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2006 May 31;4:29. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-4-29. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2006. PMID: 16734917 Free PMC article.
-
Brain nitric oxide synthase expression is enhanced in the human cervix in labor.J Soc Gynecol Investig. 2001 May-Jun;8(3):158-64. J Soc Gynecol Investig. 2001. PMID: 11390250
-
Changes in the cervical competence in preterm labour.BJOG. 2005 Mar;112 Suppl 1:23-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2005.00580.x. BJOG. 2005. PMID: 15715590 Review.
-
Changes in uterine innervation in pregnancy and during labour.Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2010 Jun;23(3):300-3. doi: 10.1097/ACO.0b013e328337c881. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2010. PMID: 20216064 Review.
Cited by
-
Toll-like receptors, cytokines & nitric oxide synthase in patients with otitis media with effusion.Indian J Med Res. 2013 Oct;138(4):523-30. Indian J Med Res. 2013. PMID: 24434259 Free PMC article.
-
Different secretion patterns of matrix metalloproteinases and IL-8 and effect of corticotropin-releasing hormone in preterm and term cervical fibroblasts.Mol Hum Reprod. 2008 Nov;14(11):641-7. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gan060. Epub 2008 Oct 15. Mol Hum Reprod. 2008. PMID: 18922847 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic hypoxia increases inducible NOS-derived nitric oxide in fetal guinea pig hearts.Pediatr Res. 2009 Feb;65(2):188-92. doi: 10.1203/PDR.0b013e31818d6ad0. Pediatr Res. 2009. PMID: 19047955 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of pattern recognition receptors in cholesteatoma.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2014 Feb;271(2):245-53. doi: 10.1007/s00405-013-2402-7. Epub 2013 Feb 26. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2014. PMID: 23440434
-
Effect of Resveratrol on Pregnancy, Prenatal Complications and Pregnancy-Associated Structure Alterations.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jan 31;12(2):341. doi: 10.3390/antiox12020341. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36829900 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Higby K, Suiter CR. A risk-benefit assessment of therapies for premature labour. Drug Saf. 1999;21:35–56. - PubMed
-
- Osmers RG, Adelmann-Grill BC, Rath W, Stuhlsatz HW, Tschesche H, Kuhn W. Biochemical events in cervical ripening dilatation during pregnancy and parturition. J Obstet Gynaecol. 1995;21:185–194. - PubMed
-
- Westergren-Thorsson G, Norman M, Bjornsson S, Endresen U, Stjernholm Y, Ekman G, Malmstrom A. Differential expressions of mRNA for proteoglycans, collagens and transforming growth factor-beta in the human cervix during pregnancy and involution. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998;1406:203–213. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

