HOXB4 enforces equivalent fates of ES-cell-derived and adult hematopoietic cells
- PMID: 16093308
- PMCID: PMC1189347
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0505624102
HOXB4 enforces equivalent fates of ES-cell-derived and adult hematopoietic cells
Abstract
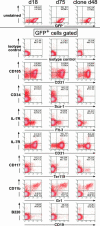
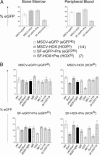
Genetic manipulation of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells is an important tool for experimental and clinical applied hematology. However, techniques that allow for gene targeting, subsequent in vitro selection, and expansion of genetically defined clones are available only for ES cells. Such molecularly defined and, hence, "safe" clones would be highly desirable for somatic gene therapy. Here, we demonstrate that in vitro differentiated ES cells completely recapitulate the growth and differentiation properties of adult bone marrow cells, in vitro and in vivo, when ectopically expressing HOXB4. Myeloid development was enforced and (T) lymphoid development suppressed over a wide range of expression levels, whereas only high expression levels of the transcription factor were detrimental for erythroid development. This indicates a close association between the amounts of ectopic HOXB4 present within a progenitor cell and and the decision to self renew or differentiate. Because HOXB4 mediates similar fates of ES-derived and bone marrow hematopoietic stem cells, the primitive embryonic cells can be considered a promising alternative for investigating hematopoietic reconstitution, in vivo, based on well defined clones. Provided that HOXB4 levels are kept within a certain therapeutic window, ES cells also carry the potential of efficient and safe somatic gene therapy.
Figures


References
-
- Glimm, H., Oh, I. H. & Eaves, C. J. (2000) Blood 96, 4185–4193. - PubMed
-
- Kondo, M., Wagers, A. J., Manz, M. G., Prohaska, S. S., Scherer, D. C., Beilhack, G. F., Shizuru, J. A. & Weissman, I. L. (2003) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 21, 759–806. - PubMed
-
- Just, U., Stocking, C., Spooncer, E., Dexter, T. M. & Ostertag, W. (1991) Cell 64, 1163–1173. - PubMed
-
- Zhang, J., Niu, C., Ye, L., Huang, H., He, X., Tong, W. G., Ross, J., Haug, J., Johnson, T., Feng, J. Q., et al. (2003) Nature 425, 836–841. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

