Atomic resolution structures of resting-state, substrate- and product-complexed Cu-nitrite reductase provide insight into catalytic mechanism
- PMID: 16093314
- PMCID: PMC1189323
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0504207102
Atomic resolution structures of resting-state, substrate- and product-complexed Cu-nitrite reductase provide insight into catalytic mechanism
Abstract
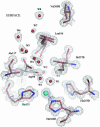
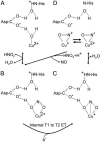
Copper-containing nitrite reductases catalyze the reduction of nitrite to nitric oxide (NO), a key step in denitrification that results in the loss of terrestrial nitrogen to the atmosphere. They are found in a wide variety of denitrifying bacteria and fungi of different physiology from a range of soil and aquatic ecosystems. Structural analysis of potential intermediates in the catalytic cycle is an important goal in understanding enzyme mechanism. Using "crystal harvesting" and substrate-soaking techniques, we have determined atomic resolution structures of four forms of the green Cu-nitrite reductase, from the soil bacterium Achromobacter cycloclastes. These structures are the resting state of the enzyme at 0.9 A, two species exhibiting different conformations of nitrite bound at the catalytic type 2 Cu, one of which is stable and also has NO present, at 1.10 A and 1.15 A, and a stable form with the product NO bound side-on to the catalytic type 2 Cu, at 1.12 A resolution. These structures provide incisive insights into the initial binding of substrate, its repositioning before catalysis, bond breakage (O-NO), and the formation of a stable NO adduct.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Side-on copper-nitrosyl coordination by nitrite reductase.Science. 2004 May 7;304(5672):867-70. doi: 10.1126/science.1095109. Science. 2004. PMID: 15131305
-
pH-profile crystal structure studies of C-terminal despentapeptide nitrite reductase from Achromobacter cycloclastes.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004 Mar 26;316(1):107-13. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.01.177. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004. PMID: 15003518
-
Alternate substrate binding modes to two mutant (D98N and H255N) forms of nitrite reductase from Alcaligenes faecalis S-6: structural model of a transient catalytic intermediate.Biochemistry. 2001 Aug 7;40(31):9132-41. doi: 10.1021/bi0107400. Biochemistry. 2001. PMID: 11478880
-
Recent structural insights into the function of copper nitrite reductases.Metallomics. 2017 Nov 15;9(11):1470-1482. doi: 10.1039/c7mt00146k. Metallomics. 2017. PMID: 28702572 Review.
-
NO production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa cd1 nitrite reductase.IUBMB Life. 2003 Oct-Nov;55(10-11):617-21. doi: 10.1080/15216540310001628672. IUBMB Life. 2003. PMID: 14711008 Review.
Cited by
-
De novo-designed metallopeptides with type 2 copper centers: modulation of reduction potentials and nitrite reductase activities.J Am Chem Soc. 2013 Dec 4;135(48):18096-107. doi: 10.1021/ja406648n. Epub 2013 Nov 19. J Am Chem Soc. 2013. PMID: 24182361 Free PMC article.
-
Fourier transform infrared characterization of a CuB-nitrosyl complex in cytochrome ba3 from Thermus thermophilus: relevance to NO reductase activity in heme-copper terminal oxidases.J Am Chem Soc. 2007 Dec 5;129(48):14952-8. doi: 10.1021/ja074600a. Epub 2007 Nov 13. J Am Chem Soc. 2007. PMID: 17997553 Free PMC article.
-
Structures of protein-protein complexes involved in electron transfer.Nature. 2013 Apr 4;496(7443):123-6. doi: 10.1038/nature11996. Epub 2013 Mar 27. Nature. 2013. PMID: 23535590 Free PMC article.
-
Unexpected Roles of a Tether Harboring a Tyrosine Gatekeeper Residue in Modular Nitrite Reductase Catalysis.ACS Catal. 2019 Jul 5;9(7):6087-6099. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.9b01266. Epub 2019 May 29. ACS Catal. 2019. PMID: 32051772 Free PMC article.
-
Visualization of membrane protein crystals in lipid cubic phase using X-ray imaging.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2013 Jul;69(Pt 7):1252-9. doi: 10.1107/S0907444913011359. Epub 2013 Jun 15. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2013. PMID: 23793151 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eady, R. R. & Hasnain, S. S. (2003) Compr. Coord. Chem. II 8, 759–786.
-
- Suzuki, S., Kataoka, K. & Yamaguchi, K. (2000) Acc. Chem. Res. 33, 728–735. - PubMed
-
- Boulanger, M. J., Kukimoto, M., Nishiyama, M., Horinouchi, S. & Murphy, M. E. P. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275, 23957–23964. - PubMed
-
- Ellis, M. J., Dodd, F. E., Sawyers, G., Eady, R. R. & Hasnain, S. S. (2003) J. Mol. Biol. 328, 429–438. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

