Phosphorylation of synapsin I by cAMP-dependent protein kinase controls synaptic vesicle dynamics in developing neurons
- PMID: 16093379
- PMCID: PMC6725302
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1573-05.2005
Phosphorylation of synapsin I by cAMP-dependent protein kinase controls synaptic vesicle dynamics in developing neurons
Abstract
In developing neurons, synaptic vesicles (SVs) undergo cycles of exo-endocytosis along isolated axons. However, it is currently unknown whether SV exocytosis is regulated before synaptogenesis. Here, we show that cAMP-dependent pathways affect SV distribution and recycling in the axonal growth cone and that these effects are mediated by the SV-associated phosphoprotein synapsin I. The presence of synapsin I on SVs is necessary for the correct localization of the vesicles in the central portion of the growth cone. Phosphorylation of synapsin I by cAMP-dependent protein kinase (protein kinase A) causes the dissociation of the protein from the SV membrane, allowing diffusion of the vesicles to the periphery of the growth cone and enhancing their rate of recycling. These results provide new clues as to the bases of the well known activity of synapsin I in synapse maturation and indicate that molecular mechanisms similar to those operating at mature nerve terminals are active in developing neurons to regulate the SV life cycle before synaptogenesis.
Figures
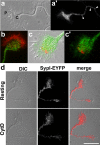
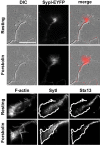



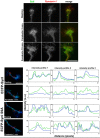


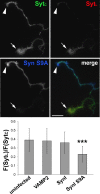
References
-
- Ahmari SE, Buchanan J, Smith SJ (2000) Assembly of presynaptic active zones from cytoplasmic transport packets. Nat Neurosci 3: 445-451. - PubMed
-
- Banker GA, Cowan WM (1977) Rat hippocampal neurons in dispersed cell culture. Brain Res 126: 397-442. - PubMed
-
- Chi P, Greengard P, Ryan TA (2001) Synapsin dispersion and reclustering during synaptic activity. Nat Neurosci 4: 1187-1193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
